Abdominal Compression Test
Adson’s
Anterior Drawer
Apprehension Test
Bear Hug Test
Belly-Off Sign
Circumduction Test
Coracoid Impingement Test
Drift Test
External Rotation Lag Sign
Gagey Hyperadbuction Test
Hawkins Impingement Sign
Hornblower's Sign
Internal Impingement Sign
Jahnke Test
Jerk Test
Kim Test
|
Lift Off Test / Lift-Off Lag Test
Load and shift
Mayo Shear Test
Napoleon Test
Neer Impingement Sign
O'Briens Test
Patte Sign
Paxinos Test
Posterior Apprehension Test
Posterior Drawer
Relocation Test
Shrug Sign
Speed's Test
Sulcus sign
Yerguson's Test
Whipple Test
Wright’s |
 |
Neer Impingement Sign
- Anterior, lateral or deep pain caused by greater tuberosity impinging on acromion during forced forward elevation.
- Best tested with examiner standing behind pt preventing scapular rotation with one hand.
- Indicates: subacromial impingement, or biceps tendonitis.
- Neer Impingement test = positive when subacromial injection of 10ml of local anesthetic (lidocaine) releaves previous pain of Impingemnt sign.
- Neer CS, Orthop Clin North Am, 1977;8:583.
|
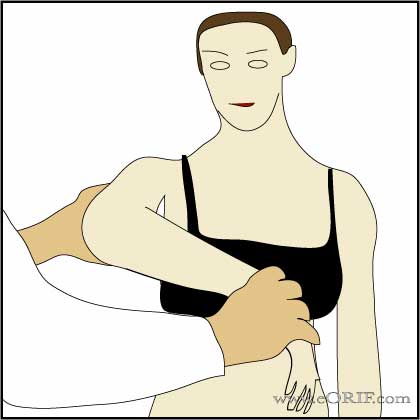 |
Hawkins Impingement Sign
- Pain caused by maximal internal rotation with the pts arm forward flexed to 90° and elbow flexed to 90°.
- Motion causes impingement of the supraspinatus on the acromion / coracoacromial ligament / coracoid process.
- Indicates: subacromial impingement,
- Hawkins RJ, AJSM 1980;8:151.
|
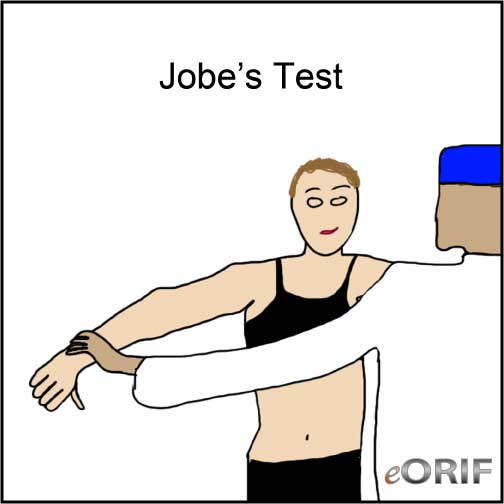 |
Jobe's Test
- Synonyms: "Empty can" test, supraspinatus test.
- Arm flexed to 90° in the scapular plain, elbow extended, thumb pointing to the floor. Patient resists downward pressure on the arm.
- Positive test: pain or weakness in the shoulder.
- Indicates: supraspinatus pathology (RTC tear vs tendinosis), or suprascapular neuropathy.
- (Jobe FW, AJSM 1982;10:336).
|
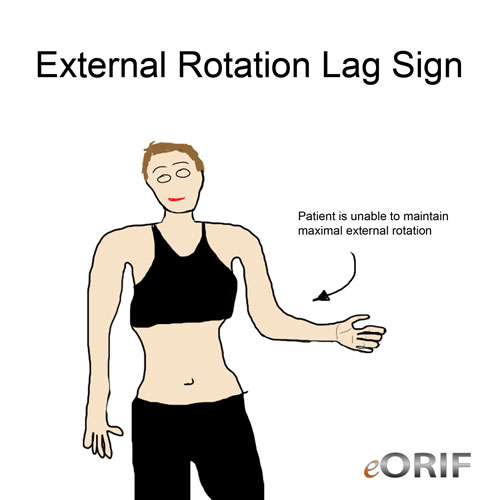 |
External Rotation Lag sign
- Synonyms:"Spring back" test, ERLS, drop test.
- Examiner holds arm in 20° forward elevation in the scapular plaine with the elbow flexed 90° and the arm in maximal external rotation.
- Postive test: inability to maintain maximal external rotation.
- Indicates: infraspinatus tear (RTC tear), or Suprascapular Nerve palsy
- (Walch GA, JBJS 1998;80B:624).
|
 |
O'Briens Test
- synonyms: Active compression teast
- Arm in forward flexion to 90°, adduction @10 degrees, and IR(thumb down). Examiner pushes down on forearm with patient resisting.
- Positive test is pain that is alleviated when the test is repeated with ER(palm up).
- Indicates: Superficial/anterior pain=AC arthritis. Deep/posterior pain=labral tear / SLAP.
- (O’Brien SJ, AM J Sports Med 1998;26;610-613).
|
| |
Anterior Slide Test
- Patient standing the hands on the hips with the thumbs pointing posteriorly. Examiner stabizes scapula with one hand on the acromion while the other hand applies force to the elbow attempting to drive the humeral head anterosuperiorly with the patient resisting the force.
- Positive Test: pain, popping, or clicking in the front of the shoulder.
- Indicates: SLAP lesion.
- Kibler WB, Arthroscopy 1995;11:296.
|
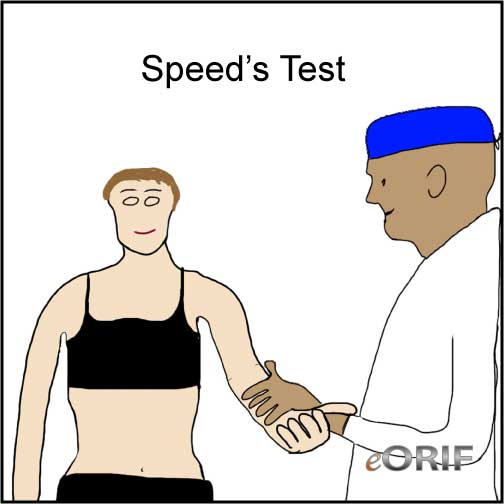 |
Speed's Test
- Arm placed in 90° of forward elevation with elbow extended and forearm supinated. Press the arm down against the patient's resistance.
- Pain in the anterior deltoid / bicipital groove indicates long head of biceps tendon pathology.
- Indicates: Biceps tendinitis or SLAPlesion.
- (Bennett WF, Arthroscopy 1998;14:789)
|
| |
Yerguson's Test
- Elbow flexed 90° with forearm pronated. Patient supinates the forearm and flex the elbow against resistance. Pain in the biciptal groove indicates long head of biceps tendon pathology.
- Holtby R, Arthroscopy 2004;20:231
|
| |
Apprehension Test
- Examiner applies anteriorly directed force to the humeral head with the shoulder in 90° abduction and the elbow in 90° of flexion while progressively increased external rotation is applied.
- Positive result: patient felling that the shoulder is going to dislocate.
- Indicates: Anterior GH Instability.
- Posterosuperior shoulder pain indicates internal impingement.
- See also Internal Impingement Sign.
|
| |
Relocation Test
- Posteriorly directed force is applied to the humeral head with patient in abduction and external rotation (Apprehension Test position).
- Positive result is relief of the feeling of impending dislocation. Indicates anterior instability.
- Posteriorsuperior shoulder pain which is relieved with relocation test indicates SLAP lesion or internal impingement.
- See also Internal Impingement Sign.
- Kvitne RS, CORR 1993;291:107
|
| |
Load and shift
- thumb used to exert a force in the direction of area tested causes pain. (12o’clock=SLAP tears, 1o’clock=superior GH ligament injury, 3 o’clock=middle GH ligament tears etc)
- Grade 0= no translation
- Grade 1=mild; head translates 0-1cm.
- Grade 2=moderate; head translates to glenoid rim, 1-2cm.
- Grade 3=severe; head translates over glenoid rim, >2cm.
- (Richards RR, JSES 1994;3:347)
|
| |
Sulcus sign
- Distraction force is applied to the arm with the patient seated with arms at the side. The magnitude of displacement is measured as the distance from the acromion to the greater tuberosity (>2cm is abnormal). Note any apprehension sensations. Compare to the contralateral limb. Any abnormalities indicated inferior instability. (Kang RW, Arthroscopy. 2009;25(8):909).
- Indicates: MDI,
- Rotator intervalmay be assessed by external rotating the humerus during the sulcus sign. If sulcus fails to improve with ER, the rotator interval is incompetent.
- Rotator interval closure best eliminates a positive sulcus sign. (Field LD, AJSM 1995;23:557).
|
| |
Circumduction Test
- Patient actively rotates the shoulder from an internally rotated and cross-body adducted position fully elevated and then to an abducted, externally rotated position and then back. Positive result is felling the joint subluxate in the interally rotated, cross-body adducted position.
- Indicates: Posterior instability,
|
| |
Posterior Apprehension Test
- Synonyms: Posterior Stress Test
- apply a posterior force to the humeral head with the arm in a forward flexed and internaly rotated position.
- Positive test is palpable or observable subluxation of the humeral head over the glenoid rim
- Indicates: Posterior instability, MDI
|
| |
Jahnke Test
- posteriorly directed force is applied to the forward flexed shoulder which is then into the coronal plane as an anteriorly directed force is applied to the humeral head. Positive result is a clunk / subluxation felt as the joint reduces from the subluxated position.
- Similar to Jerk Test.
- Indicates: Posterior instability, MDI
|
| |
Cross-body Adduction Test
- arm is maximally adducted with the arm in 90 of forward elevation. Pain localized to the AC joint indicates AC joint patholgy.
|
| |
Push-pull test
- Supine position, wrist is pulled up while the proximal humerus is pushed downward
- >50% translation of shoulder indicated MDI.
|
 |
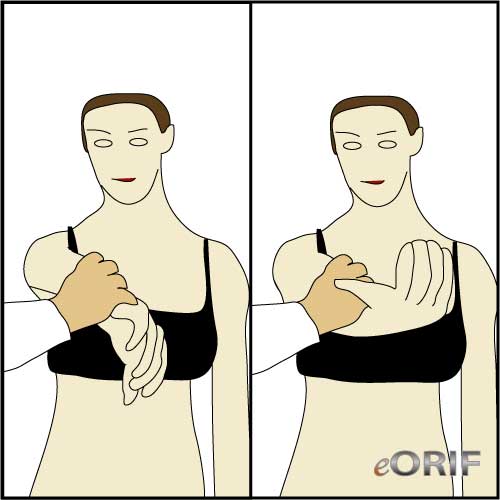
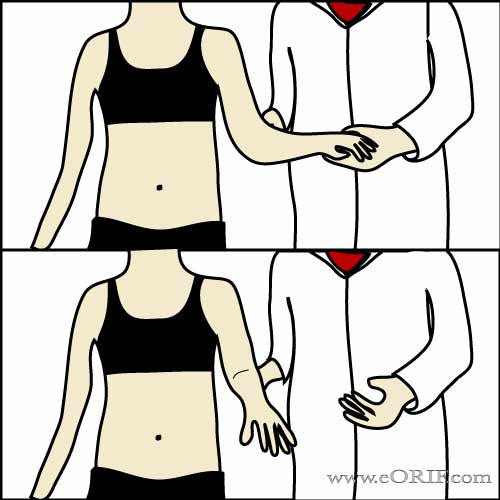
Lift Off Test
- Place the patients arm behind the back in the midline at the waist. Patient is instructed to raise the hand off the back.
- Positive result = inability to raise hand off the back. Only positive if >75% of subscapularis is torn (Barth JRH, Arthroscopy 2006;22:1076).
- Indicates: subscapularis tear.
- (Gerber C, JBJS 1991;73B:389).
- (Greis, PE, AJSM 1996;24:589).
Lift-Off Lag Test
- Examiner holds patients hand away from lumbar region in extension and maximal IR and then lets go.
- Positive result = inability to keep hand away from lumbar region.
- Indicates: subscapularis tear.
- (Hertel R, JSES 1996;5:307)
|
 |
Coracoid Impingement Sign
- Pain and clicking with passive forward flexion, adduction and internal rotation
- Indicates: Coracoid Impingement.
- (Dines DM, JBJS 1990;72Br:314) (Ferrick MR, AJSM 2000;28:117).
|
| |
Hornblower's Sign
- patient is unable to ER the arm to 90 degrees with the arm in abduction.
- Indicates massive RTC tear usually including the teres minor.
|
| |
External Rotation Lag sign
- Tests posterosuperior RTC. Arm is placed in maximal ER. Pts with a massive RTC tear will be unable to maintain the arm in the position and the arm will swing toward neutral rotation.
- Indicates massive RTC tear.
|
| |
Internal Impingement Sign
- Posterosuperior shoulder pain with arm in maximal external at 90° abduction.
- Anterior pain indicates anterior instability, posterosuperior pain indicates internal impingement.
- Patients often have relief of symptoms with posterior directed force on humeral head (relocating humeral head in center of the glenoid).
- Sensitivity=75.5%, specificity=85%; (Meister K, AM J Orthopedics 2004;33:412).
- See also Apprehension Test, Relocation test.
|
| |
Kim Test
|
| |
Jerk Test
- Position: patient sitting.
- While stabilizing the scapula and posteriorly loading the arm with it forward flexed to 90° the arm is slowly moved into abduction.
- Postive test = clunk +/- reproduction of sense of reduction.
- Indicates: Posterior instability, MDI.
- Lerat JL, Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 1994;80:461
|
| |
Adson’s
- arm at side, neck hyperextended, head turned toward affected side reproduces symptoms
|
 |
Drift Test
- Patient is unable to hold arm in a slightly externally rotated position.
- Indicates massive RTC tear usually including the infraspinatus and teres minor.
|
| |
Wright’s
- arm abducted and ER, pt takes deep breath and holds it.
|
| |
Anterior Drawer
- Patient sitting, arm in slight abduction
- Anteriorly directed force applied to posterior humeral head
- Anterior translations quantified as:
-Grade 0=no translation
-Grade 1=translation to glenoid rim
-Grade 2=translation over glenoid rim
-Grade 3=dislocation
- Indicates: Anterior GH Instability, MDI
- Gerber C, JBJS 1984;66Br:551
|
| |
Posterior Drawer
- Patient sitting, arm in slight abduction
- Posteriorly directed force applied to anterior humeral head
- Posterior translations quantified as:
-Grade 0=no translation
-Grade 1=translation to glenoid rim
-Grade 2=translation over glenoid rim
-Grade 3=dislocation
- Indicates: Posterior instability, MDI
- Gerber C, JBJS 1984;66Br:551
|
| |
Gagey Hyperadbuction Test
- Assess IGHL laxity
- Patients arm is placed in maximum abduction and internal rotation and compared to normal side.
- Increased abduction 10° greater than normal side indicates incompetence of IGHL. Normally < 105°.
- Indicates: Anterior GH Instability, MDI
- Gagey OJ, JBJS 2001;83Br:69
|
| |
Whipple Test
- Patient sitting, arm flexed 90° and adducted until hand is opposite contralateral shoulder.
- Place downward pressure on arm.
- Positve test = pain in shoulder or down arm.
- Indicates: partial thickness supraspinatus tear.
- Savoie FH, Orthop Clin North Am, 2001;32:457.
|
| |
Paxinos Test
- Compress clavicle toward the scapular spine with one hand.
- Postive result = AC jonit pain
- Indicates: AC arthritis, distal clavile osteolysis.
- Walton J, JBJS 2004 86A:807.
|
| |
Patte Sign
- Patient standing with arm in 90° of elevation in the scapular plane and 90° external roation with elbow flexed 90°.
- Patients attempts to further externally rotate arm against resistance.
- Weakness indicates infraspinatus or teres minor tear.
|
| |
Mayo Shear Test
- Patient reports posterior shoulder pain when the arm is moved up and down in elevation with an anteriorly directed force on the shoulder.
- Indicates: SLAP lesion.
|
| |
Passive Compression |
 |
Bear Hug Test
- The patients hand is placed on the opposite shoulder with the elbow anterior to the body. The examiner then applies an ER force while the patient attempts to maintain the hand on the shoulder
- Postive Result: Patient cannot hold the hand against the shoulder as examiner applies an ER force.
- Indicates: subscapularis tear.
- (Barth JRH, Arthroscopy 2006;22:1076)
|
| |
Shrug Sign
- shrug sign = inability to lift the arm to 90º abduction without elevating the whole scapula or shoulder girdle
- Patient is asked to elevate the arm until the shrug sign begins, and then the angle between the horizontal and the arm is measured with a goniometer.
- Indicates: adhesive capsulitis, associated with RTC pathology but is non-specific.
- Jia X, CORR 2008;466:2813
|
| |
Subscapularis function
- graded Napoleon test (negative, intermediate positive, and positive) and the lift-off test
- Scheibel M, Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(10): 1586-1593.
|
 |
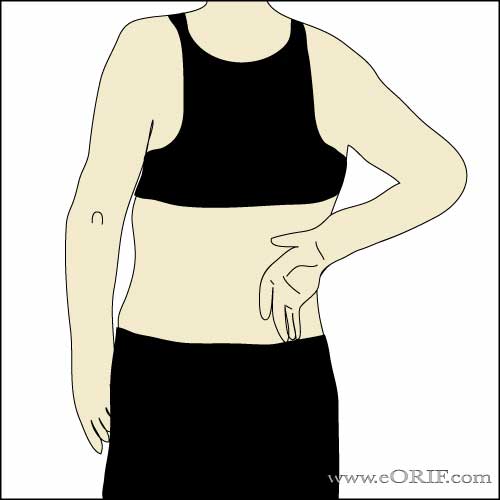
Abdominal Compression Test
- synonym: Belly-press test.
- The patients hand is place flat on their abdomen with the hand, wrist and elbow in a straight line. The patient is then instructed to press down on the abdomin.
- Postive Result: An inability to compresses the abdomen without flexing at the wrist
- Indicates: subscapularis tear.
- (Burkhart SS, Arthroscopy 2002;18:454), (Gerber C, JBJS 1996;78:1015).
Roll over image to see negative exam |
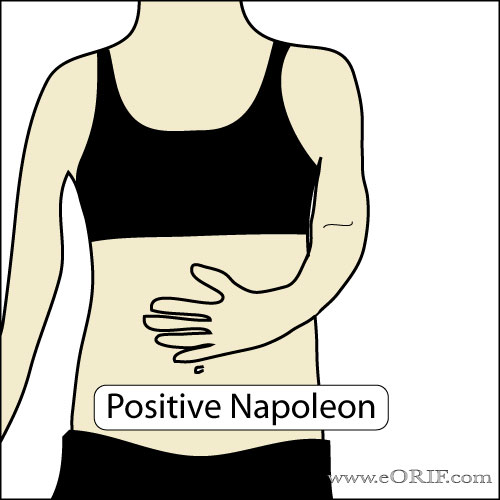 |
Napoleon Test
- Similar to Abdominal compression test.
- The patients hand is placed flat on their abdomen with the hand, wrist and elbow in a straight line. The patient is then instructed to press down on the abdomen. Negative result = wrist remains at 0° while pressing on belly, indicates normal subscapularis function.
- Postive Result: patient can press on the
belly only by flexing the wrist 90°; Intermediate result = wrist flexed 30° to 60° indicates partial function of subscapularis.
- Indicates: subscapularis tear.
- (Burkhart SS, Arthroscopy 2002;18:454)
Roll over image to see Negative exam
|
 |
Belly-Off Sign
- The patients arm is placed in flexion and maximum IR with the elbow flexed 90º. The examiner holds the elbow while positioning the hand on the abdomen. The patient is instructed to maintain the position with the wrist straight while the examiner lets go of the hand.
- Postive Result: patient's hand lifts off the abdomen when the examiner lets go.
- Indicates: subscapularis tear.
- (Scheibel M, Arthroscopy 2005;21:1229)
Roll over image to see initial positioning
Dynamic labral shear test (DLST): described for the diagnosis of superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tears. Patient reports pain and a click felt with movement of the shoulder through an arc of abduction with the shoulder externally rotated.
Upper cut test:used for diagnosis of biceps tendinopathy and SLAP tears.
|
| |
|













