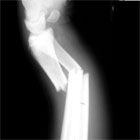
|
synonyms: Both Bone Forearm fracture, Fracture
Forearm Fracture ICD-10
A- initial encounter for closed fracture
B- initial encounter for open fracture type I or II
C- initial encounter for open fracture type IIIA, IIIB, or IIIC
D- subsequent encounter for closed fracture with routine healing
E- subsequent encounter for open fracture type I or II with routine healing
F- subsequent encounter for open fracture type IIIA, IIIB, or IIIC with routine healing
G- subsequent encounter for closed fracture with delayed healing
H- subsequent encounter for open fracture type I or II with delayed healing
J- subsequent encounter for open fracture type IIIA, IIIB, or IIIC with delayed healing
K- subsequent encounter for closed fracture with nonunion
M- subsequent encounter for open fracture type I or II with nonunion
N- subsequent encounter for open fracture type IIIA, IIIB, or IIIC with nonunion
P- subsequent encounter for closed fracture with malunion
Q- subsequent encounter for open fracture type I or II with malunion
R- subsequent encounter for open fracture type IIIA, IIIB, or IIIC with malunion
S- sequela
Forearm Fracture ICD-9
- 813.23(fracture of the radius and ulna; closed)
- 813.33(fracture of the radius and ulna; open)
Forearm Fracture Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
Forearm Fracture Anatomy
- Bicipital tuberosity should be directly opposite (180 degees) to radial styloid
- Rotational forces usually cause Fracture at different levels
- Apex volar -pronation
- Apex dorsal - suppination
- Remodeling 0.9 degrees per month, 10 degrees per year.
- Loss of forearm rotation in not seen untill a minimum of 30° of rotational maluion exists. (Kasten P, JBJS JOT 2003;17:57)
- See also Forearm Bone Anatomy.
Forearm Fracture Clinical Evaluation
Forearm Fracture Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- A/P and Lateral of radius/ulna to include elbow and wrist
- Separate views of wrist and elbow if indicated
- Template before case
Forearm Fracture Classification / Treatment
- Non-displaced: must ensure anatomic bow of the radius is maintained. RX=Short-arm cast.
- Displaced: virtually any displacement in a diaphyseal forearm fracture in an adult is an indication for ORIF. Early operative treatment improves outcomes.
- Pediatric Forearm Fracture
- Open Forearm Fracture: irrigation and debridement with immediate plate fixation (Moed BR, JBJS 68A:1008;1986). Consider external fixation with delayed ORIF if severly contaminated.
- ORIF (Chapman MW, JBJS 71A:159;1989)
- AO Classification with approaches: AO Classification
Forearm Fracture Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
Forearm Fracture Complications
Forearm Fracture Follow-up Care
- Post-op: Volar plaster splint with sling. NWB. Active elbow and finger ROM.
- 7-10 Days: Wound check, Place in funtional brace (interosseous mold). Begin active pronation/supination. Continue active elbow and finger ROM. Activity restrictions. Use for arm for light ADLS only. NWB.
- 6 Weeks: Gradually resume normal activites provided bony union is evident on xrays.
- 3 Months: Consider bone stimulator if union is not evident on xray.
- 6 Months: return to sports / full activities.
- 1Yr: Follow-up xrays, assess outcomes.
Forearm Fracture Review References
|