|
|
synonyms:
Open Fx ICD-10 / CPT
- ICD-10: Depends on specific fracture
- 7th Caracter Codes
- K- subsequent encounter for closed fracture with nonunion
- M- subsequent encounter for open fracture type I or II with nonunion
- N- subsequent encounter for open fracture type IIIA, IIIB, or IIIC with nonunion
- CPT 11010: debridement includinge removal of foreign material; open fracture/dislocation; skin and subcutaneous tissue
- CPT 11011: debridement includinge removal of foreign material; open fracture/dislocation; skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle fascia and muscle
- CPT 11012: debridement includinge removal of foreign material; open fracture/dislocation; skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle fascia, muscle and bone.
Open Fx Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Greater risk of infection and take longer to heal than comparable closed fractures.
Open Fx Anatomy
Open Fx Clinical Evaluation
Open Fx Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- Consider intrarticular sterile normal saline injection to distinguish superficial lacerations / abrasions from open wounds associated with joints. Injection must be done outside zone of injury and with large fluid bolus (50ml for knee).
- Evaluate for compartment syndrome.
Open Fx Classification / Treatment
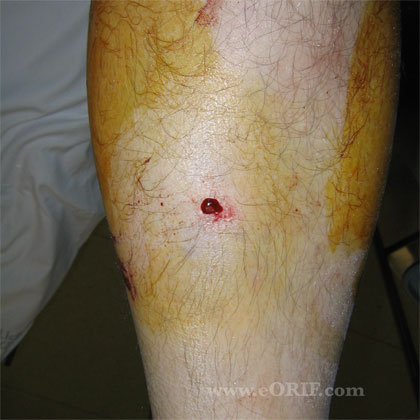
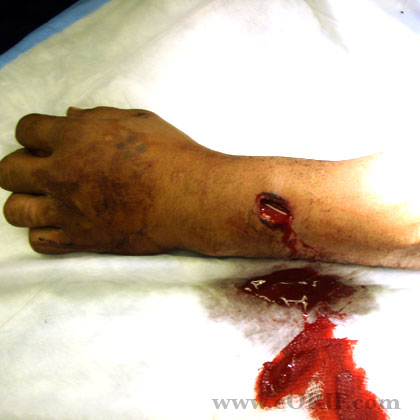
- Gustilo-Anderson Classification
-Grade I: <1cm
-Grade II: >1cm
-Grade IIIa: >10cm
-Grade IIB: requiring local or free flap coverage of the exposed bone
Grade IIIC:vascular injury requiring repair .
- Classifaction has poor interobserver agreement (Brumback RJ, JBJS 1994;76A:1162).
- IV antibiotics should be given as soon as possible. Generally Cefazolin 2 g IV Q8hrs +/- Levaquin 500mg IV QD depending on wound contamination. Historical recommendation is cefazolin +/- gentamycin. Gentamycin increases renal failure risk. Add penicillin for any wound heavily contaminated with soil.
- Antibiotic duration is 3 days for grade I and II open fx; 5 days for grade III.(Wilkins J, Orthop Clin North Am 1991;22:433).
- Tetnus vaccinationshould be given if last vaccination was > 10yrs prior or unknown. If wound is severely contaminated give vaccination in vaccination was >5yrs prior.
- Photograph the injury.
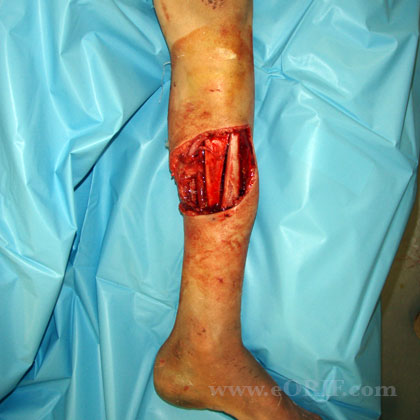
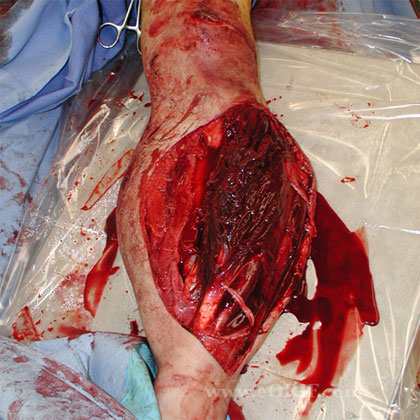
- Operative debridement should be done in a timely fashion. Exact timeline is unknown. Most important factor is when IV antibiotics where given. Associated lacerations should be extended to inspect entire zone of injury. Irrigate with low-pressure lavage (high-pressure may drive contamination into soft tissues).
- Consider wound VAC and/or antibiotic beads. Antibiotic beads made with polymethyl methacrylate impregnated with vancomycin or tobramycin.
- Exteral fixation vs internal fixation vs traction depending on fracture type and severity of soft tissue injury.
- Initial wound closure remains controversial. Recent OTA study on 415 patients with open tibial shaft fractures noted no difference in infection/union between delayed or initial closure with adequate debridement.
- Consider 4th generation cephalosporin for open fractures with pond or stream water contamination. Prophylaxis against Aeromonas.
- Open fracture Debridement CPT codes: 11010(skin, subq), 11011(skin, subq, muscle, fascia), (skin subq, muscle, fascia, bone)
Open Fx Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
Open Fx Complications
Open Fx Follow-up Care
- Early soft tissue coverage indicated when soft tissues permit. May require repeated I&D's before wound is completely free of debrie and non-vialbe tissue.
- Consider plastic surgery Flap for coverage.
Open Fx Review References
Rockwood and Green's Fractures in Adults 6th ed, 2006 |