|

|
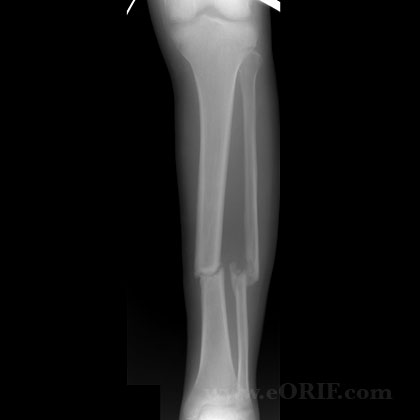
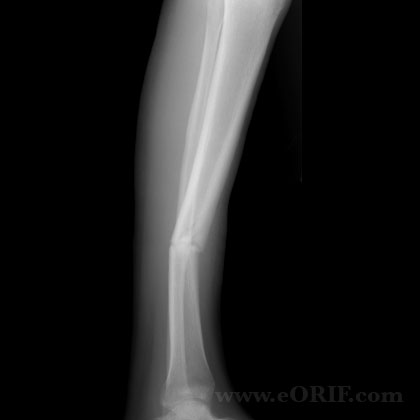
synonyms: tibial shaft nonunion, tibia nonunion
Tibial Nonunion ICD-10
Tibial Nonunion ICD-9
- 733.82 (nonunion of fracture)
Tibial Nonunion Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- There is no generally accepted definition of a tibial shaft nonunion.
- >6months old with no radiographic evidence of union
- No radiographic evidence of progress toward healing for 3 consecutive months.
- Nonsurgically treated fractures with gross clinical motion >1 month after injury.
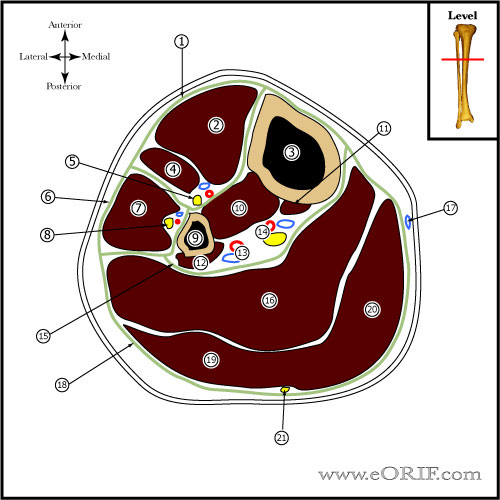
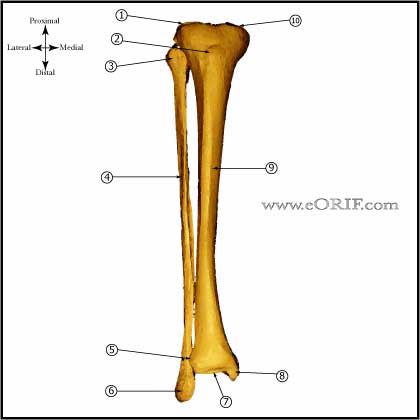
Tibial Nonunion Anatomy
- Size ranges from 30-47cm in adults, intramedullary diameter =8-15mm
- Proximal tibia has average 15 degree apex anterior angulation
- Radius of supramalleolar curvature is approximately 20cm, ie medial surface turns medially @25degrees.
- Diaphyseal blood supply is via a single nutrient artery, the proximal branch of the posterior tibial artery which passes through the most proximal portion of the tibialis posterior to obliquely enter the tibial shaft on its posterior surface in the proximal portion of the middle third of the bone. Only peripheral 1/3-1/4 of diaphyseal cortex is supplied by periosteal vessels.
- Fibula bears 6-17% of body weight, fibular head is attachment for LCL and biceps femoris, common peroneal nerve wraps around fibular neck.
- Interosseous membrane fibers run downward and laterally
Tibial Nonunion Clinical Evaluation
Tibial Nonunion Diagnositc Tests
- CT: sensitivity for detecting nonunion =100%, specificity = 62%, ie pretty high chance a CT diagnosed nonunion is actually healed. (Bhattacharyya T, JBJS 2006;88A:692)
Tibial Nonunion Classification / Treatment
- Nonunion after IM Nail: Consider nail dynamization.
- Nonunion after External Fixation: ORIF with ICBG or IM Nail. ORIF shows best outcomes (Wiss DA, JBJS 1992;74A:1279).
- Nonuion after cast treatment: reamed IM nail.
- Hypertrophic: revision with reaming to large diameter IM nail.
- Atrophic : reamed IM nail with or without ICBG, consider percutaneous injection of bone marrow aspirate (Hernigjou P, JBJS 2005;87A:1430).
- Large Osseous defects: see Bone graft options.
- rhBMP-2 (Infuse-Metronic) has shown clinical utility in spinal fusion (Glassman SD, Spine 2005;30:1694) and tibial fractures (Swiontkowski MF, JBJS 2006;88A:1258).
- BMP-7 (OP-1-Stryker): has shown clinical utlity in spinal fusion (Vaccaro AR, Spine 2005;30:2709) and tibial nonunions (Friedlaender AR, JBJS 2001;83A(suppl 1):s151).
Tibial Nonunion Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
Tibial Nonunion Complications
- Delayed union
- Nonunion
- Infection
- NVI
- Contracture
- Malunion / angular deformity
- Compartment Syndrome
- Pin infection (External fixation)
- Knee pain(IM nail)40-56% (Court-Brown CM, JOT 1997;11:103), (Keating JF, JOT 1997;11:10).
- DVT / PE
- CRPS
Tibial Nonunion Follow-up Care
- Post-op: Apply bulky Jones dressing with posterior mold to avoid equinus contracture. Elevate. Consider DVT prophyaxis.
- 7-10 Days: Remove splint, wound check. WBAT, PT, knee, ankle mobilization based on fracture stability / soft tissues.
- 6 Weeks: Xrays. Advance PT
- 3 Months: Xrays. Consider bone stimulator/nail dynamization if union is not evident. Sport specific PT.
- 6 Months: Return to full activities
- 1Yr: follow-up xrays, asssess outcomes
Tibial Nonunion Review References
- Rockwood and Green's Fractures in Adults: 2009

- Goulet JA, Templeman D: Delayed union and nonunion of tibial shaft fractures, in Springfield D (ed): Instructional Course Lectures 46. Rosemont, IL, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 1997, pp 281-291.
- Carpenter CA, Jupiter JB: Blade plate reconstruction of metaphyseal nonunion of the tibia. Clin Orthop 1996;332:23-28.
- Lonner JH, Siliski JM, Jupiter JB, Lhowe DW: Posttraumatic nonunion of the proximal tibial metaphysis. Am J Orthop 1999;28:523-528.
- Stevenson S: Enhancement of fracture healing with autogenous and allogeneic bone grafts. Clin Orthop 1998;355:S239-S246.
- Wiss DA, Johnson DL, Miao M: Compression plating for non-union after failed external fixation of open tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1992;74:1279-1285
|






