|

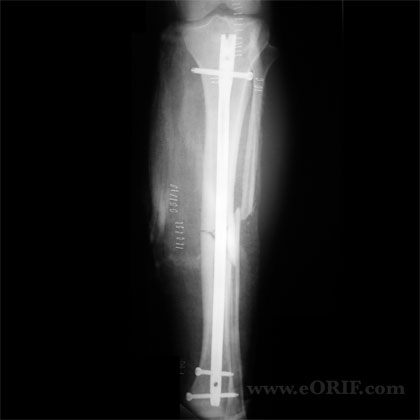
|
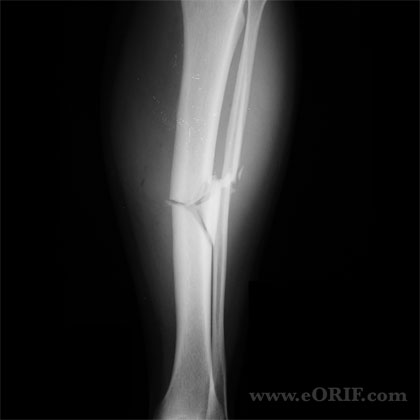
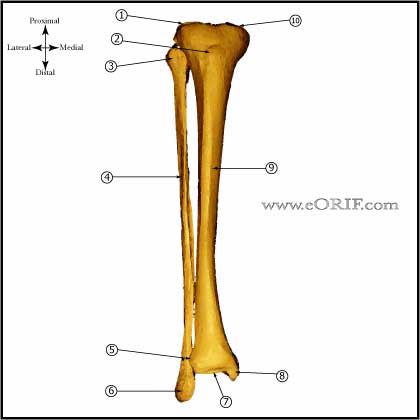
synonyms: tibial shaft fracture intramedullary nail, IM nail tibia shaft, tibial shaft IM nail
Tibial Shaft Fracture IM Nail CPT
Tibial Shaft Fracture IM Nail Indications
- high-energy fx
- modereate to severe soft-tissue injury
- unstable fracture pattern->5coronal angulation, >10sagittal angulation, >5rotation, >1cm shorteing
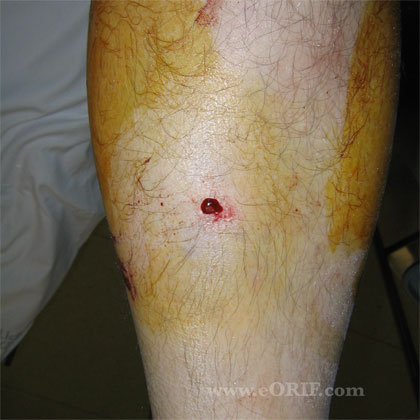
- open fx
- compartment syndrome
- ipsilateral femur fx
- inability to maintain reduction
- intact fibula
Tibial Shaft Fracture IM Nail Contraindications
- Severely contaminated open tibial shaft fracture
- External fixator with pin site infection
- External fixator in place >2 weeks (relative)
- Articular comminution: Consider ORIF vs Ilizarov.
Tibial Shaft Fracture IM Nail Alternatives
Tibial Shaft Fracture IM Nail Pre-op Planning
- Biomet VersaNail® Tibial Nail System
- Stryker T2 Tibia Nailing System Operative Technique
- Smith and Nephew TRIGEN◊ META-NAIL◊Tibial Nail System
- DepuySynthes
- Review manufacture technique guide: Does nail fit over ball-tip guidewire? What size are the proximal and distal locking screws for the chosen nail diameter? What size must the tibia be reamed to proximally. Example: Biomet low profile tibial nail=2 M/L prox screw, 2m/l distal screws, 1A/P distal screw. 8-12mm nails must have prox 6cm reamed to 12mm. 13-14mm ream 1mm over proximally. Prox screw=4.3mm drill, 5.0screws. Distal screws=3.6mm drill/4.0mmscrew for 8&9mm nails, 4.3mmdrill/5.0mm screw for 10mm+nails
- Reamed nails for closed fxs have slightly higher healing rate and less hardware failure(locking bolts) than unreamed nails. NO difference in malunion, infection, compartment syndrome, or knee pain.-OKU-7
- Discuss postoperative knee pain with patients pre-operatively.
- For Proximal 1/3 fractures see Proximal Tibial Shaft IM Nail Technique.
- Distal 1/3 fractures: reduce and fix any intraarticular extension with lag screws prior to nail insertion. ORIF any associated fibula fracture prior to IM nailing.
- Consider primary graft vs rhBMP-2 for osseous defects.
- IM Nailing may be done on a fracture table or supine on radiolucent table. Reduction of the fracture can be achieved with the fracture table, large femoral distractor, temporary two pin traveling traction, or use of an assistant / triangles.
- Blocking Screws: Consider for fractures with short proximal or distal fragments. Screw is placed in the short fragment, close to the fracture, on the concave side of the axial deformity.(Stedtfeld H JBJS 2004;86A supplement 2,:17)
- See Open Fracture.
Tibial Shaft Fracture IM Nail Technique
- Sign operative site.
- Pre-operative antibiotics, +/- regional block.
- General endotracheal anesthesia
- Supine position on radiolucent fracture table. All bony prominences well padded.
- Ensure adequate C-arm images can be taken in A/P and lateral planes.
- Prep and drape in standard sterile fashion.
- Place 2-pin traveling traction external fixator to reduce fracture and maintain reduction.
- Varify reduction. Rotation can be assess by ensuring that the second toe aligns with the tibial tuberosity.
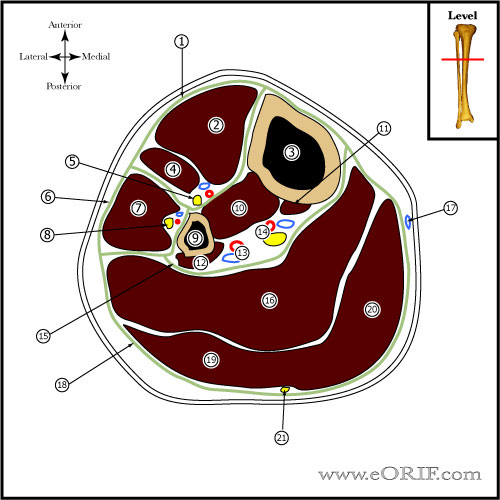
- Use bovie cord to determine entry site-proximally(just distal to articular surface) and lateral generally in line with lateral intercondylar eminence.
- Longitundinal or transverse 2-3cm incision
- Dissection medial to patellar tendon.
- Make starting point with awl.
- Place ball-tiped guidewire across fracture site.
- Ream in 0.5cm increments to 1.5mm greater than selected nail size.
- Measure nail length off guidewire.
- Place selected nail.
- Remove guide wire
- Place distal locking screws using freehand technique.
- Back slap the nail to compress the fracture site and eliminate any distraction which occured during nail placement.
- Place proximal locking screws using targeting jig.
- Remove jig
- Evaluate nail placement proximally, distally and at fracture site using c-arm.
- Irrigate.
- Close in layers.
- Apply bulky Jones dressing with posterior mold to avoid equinus contracture.
Tibial Shaft Fracture IM Nail Complications
- Knee pain 40-56% (Court-Brown CM, JOT 1997;11:103), (Keating JF, JOT 1997;11:10).
Tibial Shaft Fracture IM Nail Follow-up care
- Post-op: Apply bulky Jones dressing with posterior mold to avoid equinus contracture. Elevate. Consider DVT prophyaxis.
- 7-10 Days: Remove splint, wound check. WBAT, PT, knee, ankle mobilization based on fracture stability / soft tissues.
- 6 Weeks: Xrays. Advance PT
- 3 Months: Xrays. Consider bone stimulator/nail dynamization if union is not evident. Sport specific PT.
- 6 Months: Return to full activities
- 1Yr: follow-up xrays, asssess outcomes.
Tibial Shaft Fracture IM Nail Outcomes
- 99% union, 7% infection (Bone LB, JBJS 1986;68:877).
- 67% anterior knee pain for transtendinous nailing; 71% anterior knee pain with paratendinous nailing reported. (Toivanen JA, JBJS 2002;84A:580).
- (Finkemeier CG, JOT 2000;14:187).
Tibial Shaft Fracture IM Nail Review References
|






