|
|
synonyms:Pediatric proximal humerus fracture, shoulder fracture, broken shoulder
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture ICD-10
A- initial encounter for closed fracture
B- initial encounter for open fracture
D- subsequent encounter for fracture with routine healing
G- subsequent encounter for fracture with delayed healing
K- subsequent encounter for fracture with nonunion
P- subsequent encounter for fracture with malunion
S- sequela
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture ICD-9
- 812.0_(closed); 812.1_(open)
- 812._0(fracture of humerus, upper end, unspecified)
- 812._1(fracture of humerus, upper end, surgical neck)
- 812._2(fracture of humerus, upper end, anatomic neck)
- 812._3(fracture of humerus, upper end, greater tuberosity)
- 812._9(fracture of humerus, upper end, other; head, upper epiphysis)
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Generally occur between 11 and 17 yrs old.
- Often associated with athletic participation: direct blow during contact sport or fall onto outstretched arm.
- Also associated with aneurysmal and unicameral bone cysts and radiation therapy for malignant tumors.
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture Anatomy
- Proximal humeral physis accounts for 80% of the longitudinal growth of the humerus.
- Proximal humeral epiphysis does not begin to ossify until @ 6months old.
- Secondary ossification center for humeral head appears by 4 to 6 months of age.
- Ossification centers for greater tuberosities develop by ages 3
- Ossification centers for lesser tuberosities develop by 5
- Tuberosities fuse at 5 to 6 years old.
- Proximal humeral physis between humeral head and the shaft fuses at age 16 to 19 years.
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture Clinical Evaluation
- Shoulder pain and swelling generally after fall onto oustretched arm/shoulder.
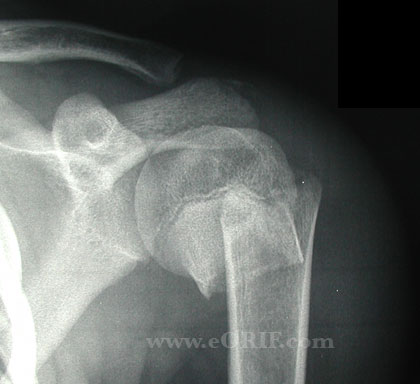
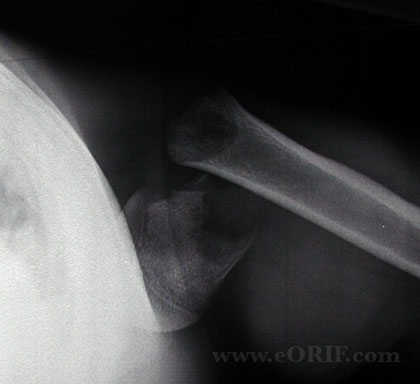
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- AP, scapular lateral and axillary views. Fracture generally easily identified in patients >6months old. Must rule out associated dislocation with axillary view.
- MRI, ultrasound or arthrogram may be needed in patietns younger than 6 months old.
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture Classification / Treatment
- Salter Harris Type I: most common in pts <5y/o.
- Salter Harris Type II: most common in pts >11y/o.
- Salter-Harris Type III: uncommon
- Salter-Harris Type IV: uncommon
- Metaphyseal fracture: most common in pts 5-11y/o.
- Acceptable Reduction:
-<5y/o: 70° angulation, 100% displacement
-5-12y/o: 40°-70° angulation
->12y/o: 40° angulation, 50% displacement.
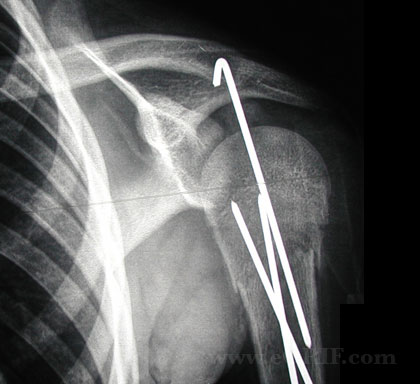
- Surgery: closed reduction, percutaneous pin fixation. Closed reduction may be prevented by interposed biceps tendon or periosteal flap.
- AO Classification
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
- Shoulder dislocation
- Brachial plexus palsy
- Clavicle Fracture
- Shoulder sepsis
- Osteomyelitis
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture Complications
- Shoulder stiffness
- Malunion
- CRPS
- Pain
- Infection
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture Follow-up Care
- Review of 30 pts age 8-15 with proximal humeral epiphyseal fractures ranging 5-100% displaced and treated with no reduction to open reduction. Despite a maximum of 2cm of shortening all pts had full ROM and no functional complaint with insignificant angular deformity. This great remodeling is due to the fact that 80% of humeral growth comes from the proximal growth plate. This author recommends open treatment for open or tented skin and neurovascular compromise only and closed treatment is unneeded.
- Baxter MP, Wiley JJ: Fractures of the proximal humeral epiphysis: Their influence on humeral growth. J Bone Joint Surg 1986;68B:570-573.
Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture Review References
- Neer CS II, Horwitz BS: Fractures of the proximal humeral epiphyseal plate. Clin Orthop 1965;41:24-31.
- Baxter MP, Wiley JJ: Fractures of the proximal humeral epiphysis: Their influence on humeral growth. J Bone Joint Surg 1986;68B:570-573°
|



