|


|
synonyms: Spinoglenoid Notch Cyst,suprascapular nerve palsy, suprascapular neuropathy
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy ICD-10
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy ICD-9
- 354.8 (other mononeuritis of upper limb)
- 354.9 (mononeuritis of upper limb, unspecified)
- 727.4 (Ganglion and cyst of synovium, tendon and bursa)
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Rare.
- More common in volleyball players (Fehrman DA, JBJS 1987;69A:260), baseballpitchers.
- May result from stretch injury (overhead activites), repetitive microtrauma, direct compression of the nerve or indirect injury to the vascular supply to the nerve.
- More common in men than women.
- Natural history of ganglion cysts about the shoulder is unknown. May enlarge over time with progressive weakness and loss of function.
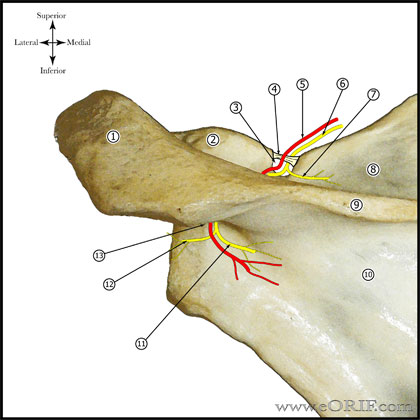
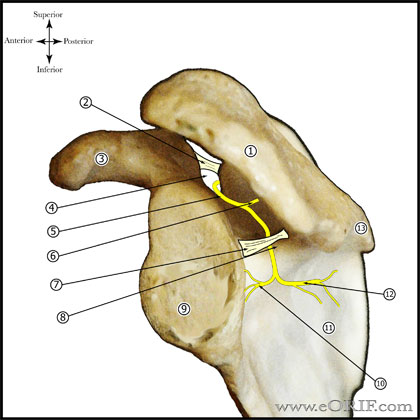
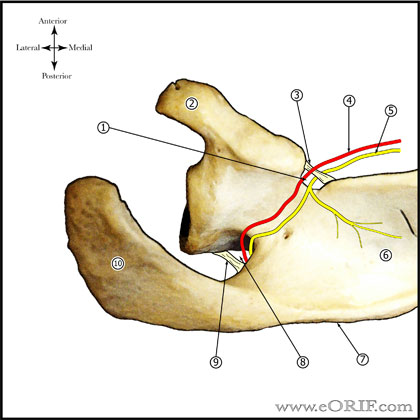
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy Anatomy
- Paralabral ganglion cyst can cause compression on the transverse scapular ligament of the spinoglenoid notch.
- Proximal compression of the suprascapular nerve (scapular notch) causes denervation of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus.
- Distal compression (spinoglenoid notch) causes denervation of the infraspinatus only.
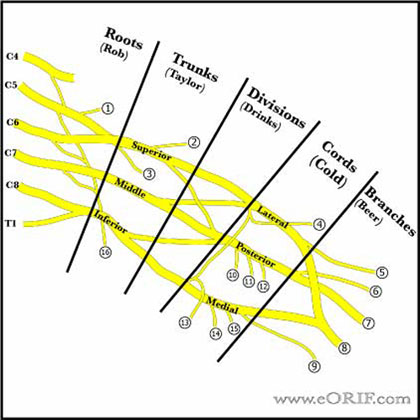
- See also Suprascapular nerve anatomy.
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy Clinical Evaluation
- Weakness and dull aching posterior shoulder pain. Supraspinatus denervation causes abduction weakness. Infraspinatus causes external rotation weakness.
- Evaluate for infraspinatus and / or supraspinatus atrophy.
- External Rotation lag signwill indicate infraspinatus weakness.
- Jobe's testmay indicated supraspinatus weakness.
- May have positive evaluation findings for SLAP Tear.
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- AP, scapular lateral and axillaryviews generally normal.
- MRI: Paralbral cysts are generally located medial to the postersuperior glenoid within the spinoglenoid notch; appear as well-defined, smoothly marginated high signal intensity on T2 images. Chronic denervation is associated with infraspinatus and supraspinatus muscle atrophy. (Tirman PF, Radiology 1994;190:653), (Inokuchni W, JSES 1998;7:223).
- EMG/NCV: indicated to confirm diagnosis. Demonstrates denervation potentials in the infraspinatus and/or supraspinatus muscles.
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy Classification / Treatment
- Unidentifiable lesion: organized physical therapy. Pain and weakness may take > one year to reach maximum improvement. PT to maintain ROM, strengthen RTC, deltoid and periscapular muscles. (Martin SD, JBJS 1997;79A:1159).
- Spinoglenoid notch cyst: arthroscopic decompression with repair of any labral injury to prevent recurrence. (Youm T, Arthroscopy 2006;22:548), (Fehrman DA, Arthroscopy 1995;11;727), (Moore TP, JSES 1997;5:455). Code as: 29823(arthroscopy shoulder; with extensive debridement) or 29807(arthroscopy shoulder with SLAP repair)
- Supracapular notch compression: shoulder arthroscopy followed by open decompression and release of the hypertrophic transverse scapular ligament.
- Ultrasound or CT guided aspiration has also been previously reported.
Open Spinoglenoid Notch Decompression Technique
- Perform shoulder arthroscopy and repair any labral lesion first.
- 4-6cm longitudinal incision 3cm medial to the posterolateral corner of the acromion.
- Dissect under 2.5x/3.5x loop magnification down to deltoid. Split deltoid fibers beginning at the scapular spine.
- Retract superior edge of the infraspinatus inferiorly.
- Identify suprascapular nerve, suprascapular artery and spinoglenoid notch cyst in the spinoglenoid notch.
- Excise the cyst.
- Irrigate.
- Repair deltoid fascia.
- Close in layers.
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy Complications
- Recurrence
- Suprascapular nerve injury
- Continued pain
- Continued muscle atrophy
- Shoulder arthroscopy risks
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy Follow-up Care
- 7-10 Days post-op: start PT. Avoid stress the superior labrum for 6 wks if concomitant SLAP/labral repair was done.
- Supraspinatus and infraspinatus atrophy often persist, even after decompression of associated cysts.
- Spinoglenoid notch cyst decompression generally resolves associated shoulder pain.
- 100% successful outcomes for arthroscopic labral repair without formal cyst excision (Youm T, Arthroscopy 2006;22:548) .
Suprascapular Nerve Palsy Review References
- Piatt BE, JSES 2002;11:600
- Antoniadis G, J Neurosurg 1996;85:1020
- Romeo AA, JAAOS, 1999;6:358
- Cummins CA, JBJS 2000;82A:415
- Martin SD, JBJS 1997;79A:1159
|








