|
|
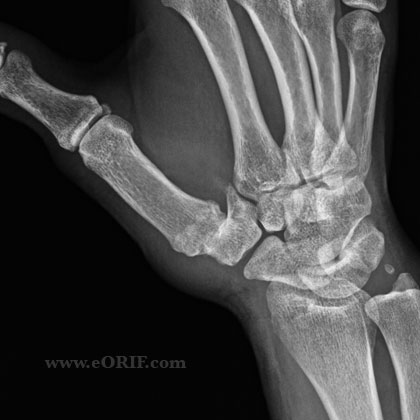
synonyms: thumb cmc arthritis, thumb carpometacarpal arthritis. treziometacarpal arthritis
Basilar Joint Arhtritis ICD-10
Basilar Joint Arhtritis ICD-9
Basilar Joint Arhtritis Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Degeneration of the deep anterior oblique ligaments (beak ligament) leads to the development of osteoarthritis of the TM joint.
- Common
- Women >> men.
- Natural history: severe thumb pain may gradually improve as the disease worsens and thumb CMC motion decreases.
Basilar Joint Arhtritis Anatomy
- Major stabilizers of the trapeziometacarpal joint = anterior oblique (beak) ligament, dorsal radial ligament.
Basilar Joint Arhtritis Clinical Evaluation
- Tenderness along the thumb trapeziometacarpal joint. Pain and weakenss with pinch and gripping activities.
- Decreased radial and palmar thumb abduction.
- Night pain common.
- Grind Test: axial compression, flexion, extension and circumduction reproduces patients symptoms.
- Evaluate for MCP hyperextensibility. MCP hyperextension greater the 20° may compromise LRTI outcomes. Consider fusion.
- Allen's test indicated to determine patency of ulnar artery if surgery involving the radial artery is considered.
Basilar Joint Arhtritis Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- Posteroanterior (PA) 30° oblique stress view , a lateral view, and a Robert's (pronated anteroposterior [AP]) view.
Basilar Joint Arhtritis Classification / Treatment
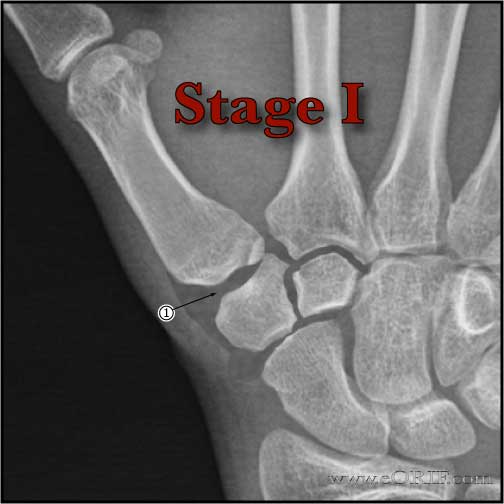
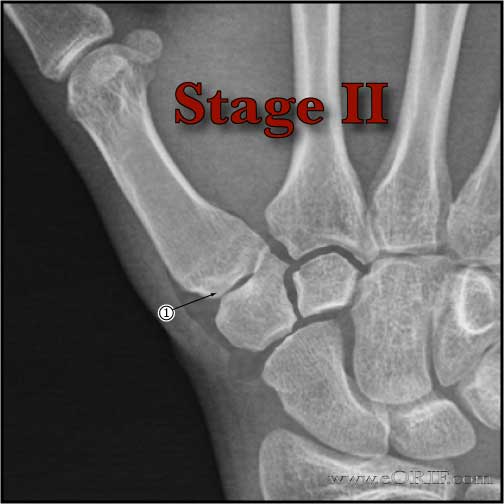
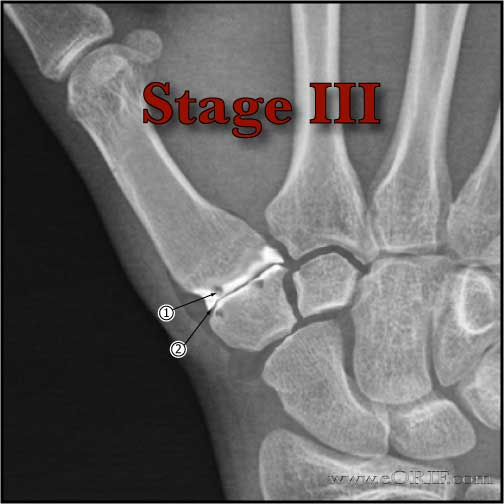
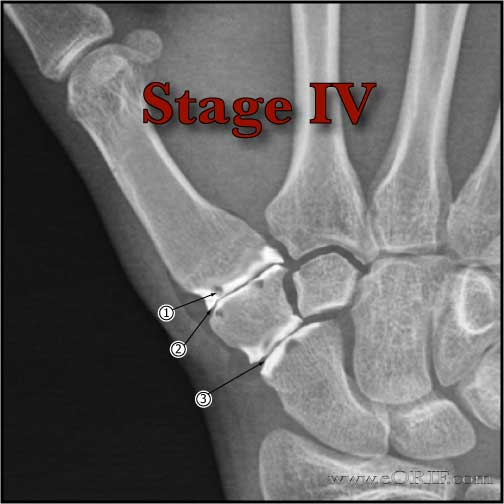
- Eaton Littler Staging of Basalar joint arthritis (Eaton RG, J Hand Surg 1984;9A:692).
- Initial treatment = NSAIDs, corticosteriod injection, splinting, activity modifications.
- Stage I (Normal joint with the exception of possible widening from synovitis) = Ligament reconstruction or metacarpal extension osteotomy
- Stage II (Joint space narrowing with debris and osteophytes less than 2 mm in size.) = LRTI, or trapeziometacarpal fusion or implant arthroplasty.
- Stage III (Joint space narrowing with debris and osteophytes greater than 2 mm in size) Treatment = LRTI, or trapeziometacarpal fusion or implant arthroplasty.
- Stage IV (Scaphotrapezoidal joint space involvement in addition to narrowing of the trapeziometacarpal joint) Treatment = LRTIwith complete trapezium excision.
Basilar Joint Arhtritis Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
- DeQuervain's disease
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Stenosing flexor tenosynovitis
- Scaphotrapezial arthritis
- Subsesamoid arthritis
LRTI Complications
- Continued pain. (generally from unaddressed scaphotrapezial or scaphotrapezoidal disease).
- Instability
- Thumb metacarpal subsidence
- Poor grip strength
- Numbness (sensory branch of Radial nerve injury).
LRTI Follow-up care
- Post-op: thumb spica splint, elevation, NWB
- 7-10 Days: wound check, place in short arm thumb spica cast
- 4 Weeks: remove k-wires. Removable thumb spica splint, with gentle assisted range-of-motion (AROM) exercises.
- 6 Weeks: Wean out of splint. Begin strengthening exercises.
- 3 Months: assess outcomes, Xrays to assess arthroplasty space height.
- 6 Months: assess outcomes
- 1Yr: assess outcomes. Functional improvement can occur up to 1 year postoperatively.
Basilar Joint Arhtritis Review References
|






