|

|
synonyms: drop foot
Peroneal Nerve Palsy ICD-10
A- initial encounter
D- subsequent encounter
S- sequela
Peroneal Nerve Palsy ICD-9
- 956.3 Injury to peripheral nerve: peroneal nerve
Peroneal Nerve Palsy Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Associated with knee dislocations
- Superficial peroneal nerve palsy may occur during inversion ankle sprains (O'Neal PJ, JBJS 2007;89A:979)
- May occur after TKA; mainly in patients with severe valgus deformity.
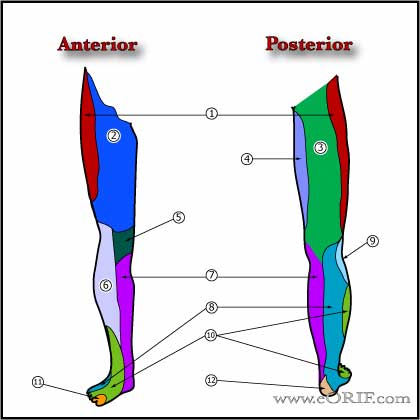
Peroneal Nerve Palsy Anatomy
- Peroneal nerve is superficial to the lateral head of the gastrocnemius.
- Mean distance from the bony posterolateral corner of the tibia to the nerve is 1.49 cm, with no distance less than 0.9 cm. Clarke HD, J Arthroplasty 2004;19:40-44)
- Distance from the posterolateral tibia to nerve is greater in larger legs.
Peroneal Nerve Palsy Clinical Evaluation
Peroneal Nerve Palsy Xray / Diagnositc Tests
Peroneal Nerve Palsy Classification / Treatment
- Acute laceration: nerve repair
- Initial treatment: ankle-foot-orthosis
- Chronic peroneal nerve palsy / foot drop: transfer of the tibialis posterior to the dorsum of the foot. (Wagenaar FC, Louwerens JW. Posterior tibial tendon transfer: results of fixation to the dorsiflexors proximal to the ankle joint. Foot Ankle Int. 2007 Nov;28(11):1128-42)
- Peroneal Nerve Decompression CPT-64708
- TKA in patient with large valgus deformity and flexion contracture has increased risk for peroneal nerve injury. Treatment: remove tight dressings, flex knee and extend the hip to decrease peroneal nerve tension.
Peroneal Nerve Palsy Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
Peroneal Nerve Palsy Complications
Peroneal Nerve Palsy Follow-up Care
Peroneal Nerve Palsy Review References
- Garozzo D, Ferraresi S, Buffatti P. Surgical treatment of common peroneal nerve injuries: indications and results. A series of 62 cases. J Neurosurg Sci. 2004 Sep;48(3):105-12
- Niall DM, Nutton RW, Keating JF. Palsy of the common peroneal nerve after traumatic dislocation of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005 May;87(5):664-7.
- Ozkan T, Tuncer S, Ozturk K, Aydin A, Ozkan S. Tibialis posterior tendon transfer for persistent drop foot after peroneal nerve repair. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2009 Mar;25(3):157-64. Epub 2008 Nov 26. View Abstract at PubMed
- Vigasio A, Marcoccio I, Patelli A, Mattiuzzo V, Prestini G. New tendon transfer for correction of drop-foot in common peroneal nerve palsy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008 Jun;466(6):1454-66
-
Schinsky MF, Macaulay W, Parks ML, et al: Nerve injury after primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2001;16:1048-1054.
-
Asp JP, Rand JA: Peroneal nerve palsy after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1990;261:233-237.
-
Clarke HD, Schwartz JB, Math KR, Scuderi GR: Anatomic risk of peroneal nerve injury with the "pie crust" technique for valgus release in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2004;19(1):40-44.
|


