|
synonyms:
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture ICD-10
A- initial encounter for closed fracture
B- initial encounter for open fracture
D- subsequent encounter for fracture with routine healing
G- subsequent encounter for fracture with delayed healing
K- subsequent encounter for fracture with nonunion
P- subsequent encounter for fracture with malunion
S- sequela
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture ICD-9
- 812.21 (closed fracture of humeral shaft)
- 812.31 (open fracture of humeral shaft)
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- May occur from direct blows, falls, MVA, child abuse, birth trauma.
- More common in children under 3y/o and over 12y/o.
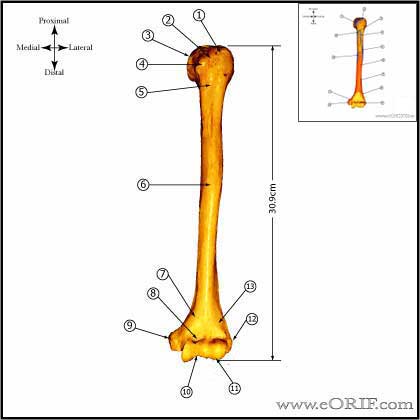
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture Anatomy
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture Clinical Evaluation
- Pain and swelling in arm after trauma / fall onto outstretched arm. OFten gross deformity.
- Document NV exam before and after any treatment.
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- A/P and lateral views of the humerus.
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture Classification / Treatment
- Location: proximal 1/3, middle 1/3, distal 1/3. Pattern: spiral oblique, transvers, segmental.
- Acceptable Alignment:
- <5y/o: 70° angulation, 100% displacement.
-5-12y/o: 40-70° angulation
->12y/o: 40° angulation, 50% displacement, bayonet appostion with <2cm shortening is acceptable.
- Birth Fracture: Splint in extension. Primary complication is internal rotation deformity.
- Acceptable aligment: plaster coaptation splint with a collar and cuff sling. May need sedation for reduction. Document NV exam after splinting.
- Unacceptable alignment: Smooth flexible IM rods (2mm) placed retrograde throught the epicondyles.
- Open fracture or extensive comminution: consider unilateral external fixation or flexible IM nails.
- Holstein-Lewis fracture = short oblique fracture of the distal 1/3 of the humerus noted for potential for radial nerve palsy after closed reduction. (Holstein A, JBJS 1963;45A:1382).
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
- Supracondyle humerus fracture
- Clavicle fracture
- Proximal humeral physeal fracture
- Shoulder dislocation
- Brachial plexus palsy
- Septic shoulder / osteomyelitis
- Child Abuse
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture Complications
- Malunion: Internal rotation deformity can cause limitations in throwing and facial hygiene.
- Radial nerve palsy
- Infection
- Delayed union / nonunion
- Fixation failure
- Compartment Syndrome
- Median/ulnar nerve palsy: uncommon
- Limb length discrepancy: overgrowth of the injury extremity is common, generally <1cm.
- CRPS
- Refracture
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture Follow-up Care
- Follow weekly to ensure alignment is maintained and coaptation splint is fitting properly.
- Generally heals in 6-8 weeks.
- Avoid contact sports until 6 months after injury.
Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fracture Review References
- Beaty JH, ICL 1992;41:369
- °
|