 |
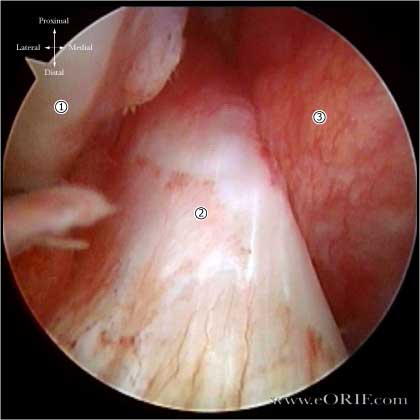
Arthroscopic Image of Normal Anterior cruciate ligament.
- Lateral Femoral Condyle
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament
|
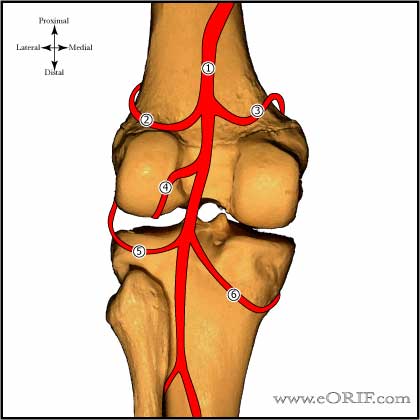 |
ACL Blood Supply
Posterior view of the knee demonstrating blood supply.
- Popliteal artery
- Superior lateral genicular artery
- Superior medial genicular artery
- Middle geniculate artery
- Inferior lateral genicular artery
- Inferior medial genicular artery
|
| |
ACL Innervation
- Posterior articular nerve (a branch of the tibial nerve) (Kennedy JC, JBJS 1974;56A:223). Normal ACL has proprioceptive senses that help protect the knee joint during use which are lost after reconstruction
|
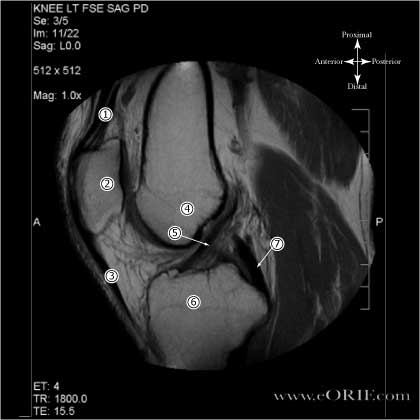 |
Proton Density MRI of Normal ACL
- Quadriceps tendon
- Patella
- Patellar ligmanet
- Distal femur (notch area)
- ACL
- Tibial Plateau
- PCL
Sagittal FSE PD image
|
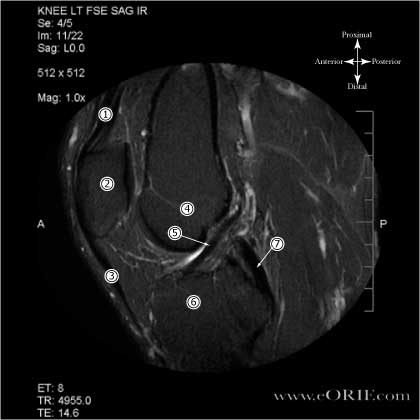 |
Inversion Recovery MRI of Normal ACL
- Quadriceps tendon
- Patella
- Patellar ligmanet
- Distal femur (notch area)
- ACL
- Tibial Plateau
- PCL
Sagittal FSE IR image
|
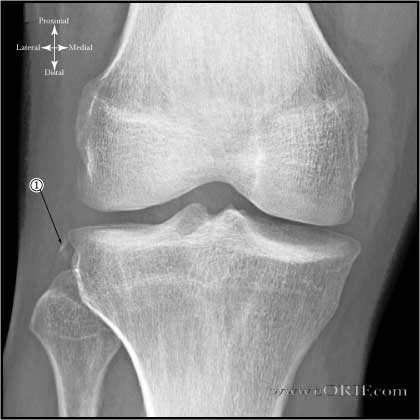 |
A/P Image of a right knee demonstrating a Segond Fracture.
- Segond fracture (avulsion fracture of lateral tibial plateau) is pathognomonic of ACL injury. Located posterior to Gerdy's tubercle and superior and anterior to the fibular head (avulsion of lateral capsule).
|
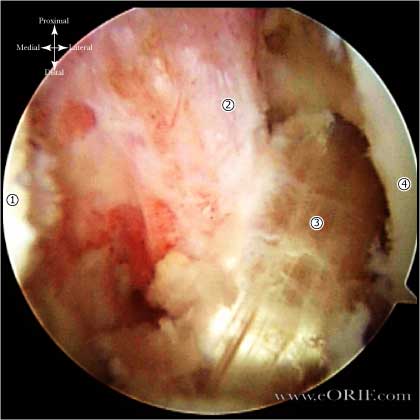 |
ACL Hamsting Reconstruction
- Medial Femoral Condyle
- PCL
- Hamsting ACL Reconstruction
- Lateral Femoral Condyle
|
| |
- Peak anteromedial bundle ACL relative strain is greater in female than male knees.
- ACL cross-sectional area is smaller and lateral tibial slope is greater in female knees.
- Lipps DB, Oh YK, Ashton-Miller JA, Wojtys EM. Morphologic characteristics help explain the gender difference in peak anterior cruciate ligament strain during a simulated pivot landing. Am J Sports Med. 2012 Jan;40(1):32-40.
|






