|
synonyms:
Swan Neck Deformity ICD-10
Swan Neck Deformity ICD-9
- 736.22 Swan Neck Deformity 736.22
Swan Neck Deformity Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
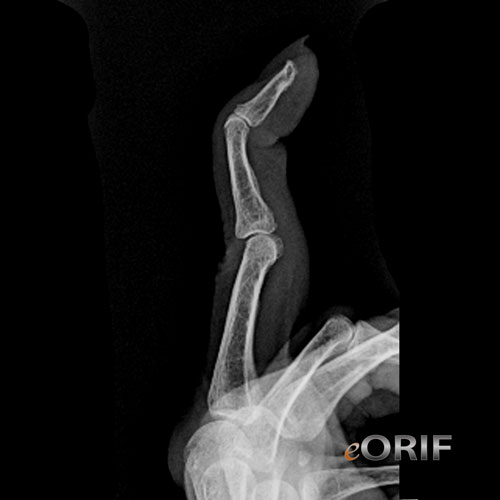
- Characterized by hyperextension of the PIP joint and flexion of the DIP joint
- Affects approximately 14% of patients with established rheumatoid arthritis (Boyer MI, JAAOS 1999;7:92)
- Generally caused by tenosynovitis and synovitis in the finger and PIP joint
Swan Neck Deformity Anatomy
- The volar plate, collateral ligaments, and flexor digitorum superficialis allows the PIP joint to hyperextend due to extensor mechanism forces. The deforming forces may be accentuated by intrinsic contracture/tightness related to MCP joint flexion and volar subluxation.
- DIP joint synovitis may rupture the terminal extensor tendon which worsens the PIP hyperextention
Swan Neck Deformity Clinical Evaluation
- hyperextension of the PIP joint with concomitant flexion of the DIP joint
Swan Neck Deformity Xray / Diagnositc Tests
Swan Neck Deformity Classification / Treatment
- Nalebuff Type I: flexible hyperextension of the PIP joint. RX:
- Nalebuff Type II: tightness of the intrinsic muscles causes limitation of PIP joint flexion when the MCP joint is maintained in extension.
- Nalebuff Type III: limited PIP joint flexion in all MCP joint positions due to the inability of the lateral bands to translate volar to the axis of rotation of the PIP joint.
- Nalebuff Type IV: destruction of the articular surface of the PIP joint
- Treatment options: see (Boyer MI, JAAOS 1999;7:92)
Swan Neck Deformity Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
Swan Neck Deformity Complications
- Boyer MI, JAAOS 1999;7:92
Swan Neck Deformity Follow-up Care
Swan Neck Deformity Review References
|