|

|
synonyms: avascular necrosis of the humeral head, shoulder avn, shoulder osteonecrosis
Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head ICD-10
- M87.021 - Idiopathic aseptic necrosis of right humerus
- M87.022 - Idiopathic aseptic necrosis of left humerus
- M87.029 - Idiopathic aseptic necrosis of unspecified humerus
- See Osteonecrosis shoulder ICD-10 codes.
Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head ICD-9
- 733.41(shoulder) asceptic necrosis of bone-humeral head
Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Can be posttraumatic or nontraumatic.
- Postraumatic: generally after proximal humerus fracture with disruption of blood supply to humeral head
- Nontrauamtic: associated with sickle cell anemia, corticosteriod use ,
- Most commonly adults 20-50yrs old
- Etiology: EtOH or prolonged high dose steriods. Other risk factors: sickle cell, dysbarism, Gaucher's disease, trauma, high-dose radiation, thrombophilia, protein S & C defiencies, hypofibrinolysis.
- Thought to be due to altered circulating lipids and coagulation mechanisms.
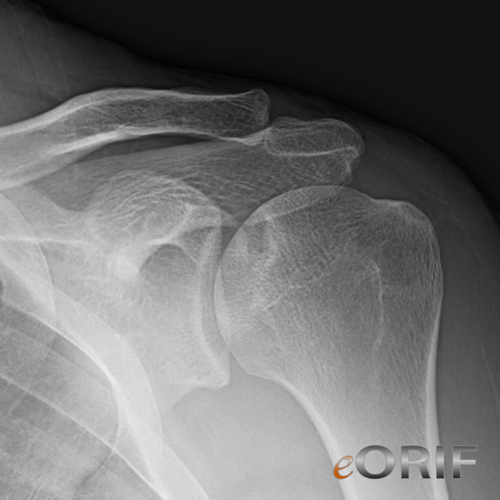
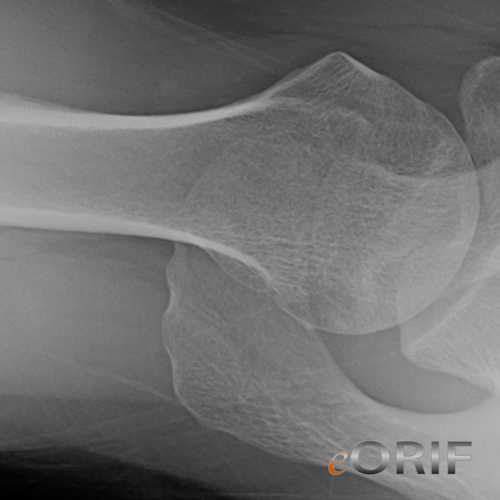
- Marrow death occurs 6-12 hrs after ischemia, radiographic changes appear after 3 months, articular collapse within 6-12 months in 80% of patients with clinical AVN.
Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head Anatomy
Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head Clinical Evaluation
- Gradually progressive shoulder pain.
- Progessive stiffness and loss of motion.
- Generally normal strength
Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- AP, scapular lateral and axillary views. See Shoulder Xray.
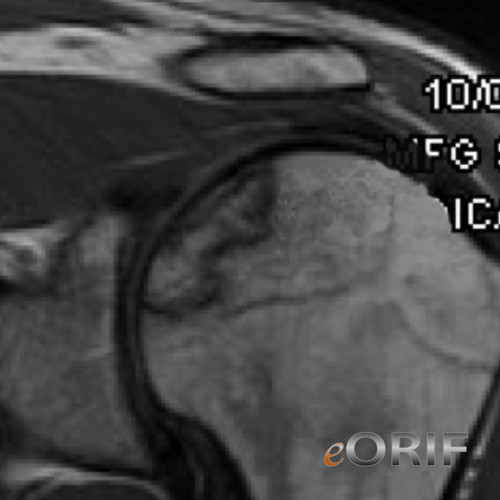
- MRI: If suspected but not seen or if only in one shoulder MRI is indicated. MRI sensitivity and specificiaty=95% for early AVN. Not good for estimating the extent of lesion.
- CT is the best technique to determine area of bone death.
- Bone scans are sensitive but have large number of false positives and have no advantage over MRI
- Evaluation should include lipid levels and possible screening for decreased levels of protein C and S and antithrombin III and increased levles of plasminogen activatoter inhibitor-1.
Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head Classification / Treatment
Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
- Shoulder osteoarthritis
- Tumor
- Infection
TSA Complications
- Overall 12% incidence (Chin PY, JSES, 2006;15:19) (14%=Cofield RH, ICL 1990;39:449)
- Instability / soft tissue imbalance:
- Rotator cuff tear (Hattrup SJ, JSES, 2006;15:78)
- ectopic ossification
- glenoid loosening
- Peri-Prosthetic fracture (0.5%-3%)
- nerve injury (Lynch NM, JSES 1996;5:53)
- infection: <1% with peri-operative antibiotics
- humeral loosening
- Long-head of biceps rupture
Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head Follow-up Care
- Dependent on stage and treatment.
Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head Review References
|




