|
Ballistic Injury: extent of mechanical damage is primarily determined by the kinetic energy (KE = 1/2MV2), where (M) is mass or caliber of the projectile and (V) is velocity.
3 Phases of Blast (bomb) injury
- Primary phase: high-pressure shock wave followed by blast wind.
- Secondary phase: Surrounding objects are turned into projectiles causeing injury. Biologic projectiles (bone fragments from the bomber or surronding people) but victums at increased risk for disease transmission. Consider Hep B vaccination, anti-retroviral therapy. (Wong JML, J Trauma 2006;60:402).
- Tertiary phase: Injuries caused as victums are thrown against solid ojects.
Direct damage is caused by the projectile’s physical size and shape.
Indirect injury is caused by the temporary cavity produced as tissue accelerates away from the bullet’s path. Indirect injury force can cause wedge shaped fractures
Clothing increase the size and depth of the indirect injury and can cause more severe fractures.
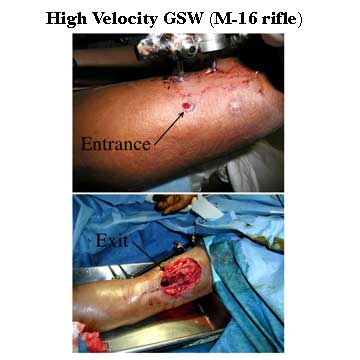
Firearm Classification and Treatment (based on the speed at which a bullet leaves the gun barrel)
- high-velocity (> 2,000 feet per second; all rifles): 41% infection risk. Prompt administration of first-generation cephalosporin; continued antibiotics for one to three days. Do not aminoglycosides or penicillin. Serial Debridement with delayed wound closure in 3-5 days.
- low-velocity (< 2,000 feet per second; handguns):9.5% infection risk.
- Shotguns are high-energy ifwithin 10 feet. Shotgun cartridges contain wadding that can embed within soft tissues and become an infection nidus.
Gun Shot Wound Treatment
|