|

|
synonyms: glenoid neck fracture, scapular neck fracture
Glenoid Neck Fracture ICD-10
- S42.151A - Displaced fracture of neck of scapula, right shoulder, initial encounter for closed fracture
- S42.152A - Displaced fracture of neck of scapula, left shoulder, initial encounter for closed fracture
- S42.153A - Displaced fracture of neck of scapula, unspecified shoulder, initial encounter for closed fracture
- S42.154A - Nondisplaced fracture of neck of scapula, right shoulder, initial encounter for closed fracture
- S42.155A - Nondisplaced fracture of neck of scapula, left shoulder, initial encounter for closed fracture
- S42.156A - Nondisplaced fracture of neck of scapula, unspecified shoulder, initial encounter for closed fracture
A - initial encounter for closed fracture
B - initial encounter for open fracture
D - subsequent encounter for fracture with routine healing
G - subsequent encounter for fracture with delayed healing
K - subsequent encounter for fracture with nonunion
P - subsequent encounter for fracture with malunion
S - sequela
Glenoid Neck Fracture ICD-9
- 811.03 Fracture of scapula, closed: glenoid cavity and neck of scapula
Glenoid Neck Fracture Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
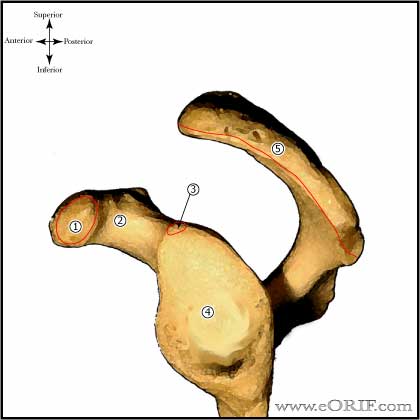
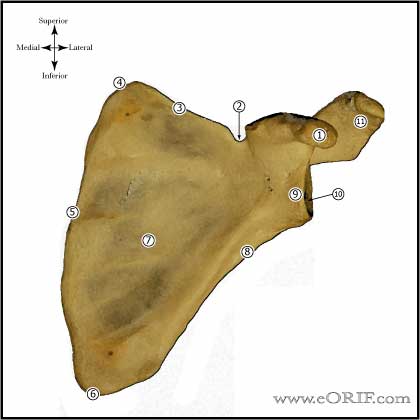
Glenoid Neck Fracture Anatomy
- Long head of triceps tendon typically displaces the glenoid inferiorly and laterally.
- Avoid quadrangular space during posterior exposure.
Glenoid Neck Fracture Clinical Evaluation
- These are typically high enegery injuries, assessment should begins with the A,B,C's.
- C/O shoulder pain after trauma.
- Evaluate for tenderness, ecchymosis, soft tissue injury.
- Document axillary, median, ulnar, radial nerve function and radial pulse.
Glenoid Neck Fracture Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- Grashe view (true A/P of scapula), scapular lateral, axillary view.
- CT scan generally indicated to fully assess fracture.
Glenoid Neck Fracture Classification / Treatment
- Nondisplaced / minimally displaced : immobilization in a sling for 1 wk followed by progressive ROM and physical therapy.
- Displaced (displacement >1cm, >40 degrees of angulation in the coronal or sagittal planes): ORIF
Glenoid Neck Fracture Technique
- Contraindications: severely comminunted fractures which preclude satisfactory fixation.
- It is important to review scapular anatomy before surgery. Look at a skeleton and review areas in which fixation can be placed in the scapula.
- Consent for iliac crest bone graft if needed.
- Pre-op antibiotics, SCD's on bilateral lower extremities
- General endotracheal anesthesia
- Folley catheter
- Lateral decubitus position; axillary role; pad all bony prominences
- Prep and drap in standard sterile fashion
- Incision over lateral spine of the scapula alone posterior aspect of acromion.
- Expose posterior deltoid and subperiosteally reflect it off its origin from the scapular spine and acromion. This exposes the underlying infraspinatus and teres minor.
- Incise inferior 1/2 of the infraspinatus insertion and open the interval between the infraspinatus and teres minor. This exposes posterior capsule.
- Infraspinatus is reflect of the caspule and retracted superiorly.
- Posterior capsule is incised from the humerus and elcvated superiorly exposing the glenoid. Fukuda retractor can be used to hold humeral head anteriorly.
- Fracture is identified, reduced and fixed using standard AO techniques. Fixation is generally provided with 3.5mm reconstruction plates, and / or 3.5mm or 4.0mm cannulated screws.
- Keep in mind the majority of the scapula is paper thin. Adequate bone stock to hold screws can be found: in the glenoid neck, coracoid process, base of the scapular spine, and lateral border of the scapular body.
- Irrigate
- Close in layers
Glenoid Neck Fracture Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
- >80% incidence of associated injury
- Rib fracture, pulmonary contusion
- Clavicle Fracture
- Proximal Humerus Fracture
- Scapular Fracture
- Acromioclavicular dislocation
- Sternoclavicular dislocation
- Scapulthoracic dissociation
- Floating Shoulder
Glenoid Neck Fracture Complications
- Nerve injury: axillary
- Glenohumeral arthritis
- Nonunion
- Malunion
- Infection
- Stiffness
Glenoid Neck Fracture Follow-up Care
- Shoulder immobilizer with gentle pendulum, elbow/wrist/hand ROM immediately
- F/U at 7-10 days. Start physcial therapy for gentle ROM exercises at first post-op visit.
- ROM and strengthening are advanced dependent on fracture type, fixation and healing. Generally patients remain in the sling for 6 weeks. Has limited use of the extremiity for 10-12 weeks and must refrain from heavy physical activity for 4-6 months.
- Shoulder Outcome measures.
Glenoid Neck Fracture Review References
- Goss JAAOS 3:22;1995
- Ada JR, CORR 1991;269:174
- Goss TP, JSES 1994;3:42
- Wirth MA, in Complex and Revision Problems in Shoulder Surgery, 2005. ISBN-10: 0781746582
- Rockwood and Green's Fractures in Adults 6th ed, 2006
- OKU - Shoulder and Elbow 2nd ed, 2002
|



