|
synonyms:
DIP Dislocation ICD-10
A- initial encounter
D- subsequent encounter
S- sequela
DIP Dislocation ICD-9
DIP Dislocation Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
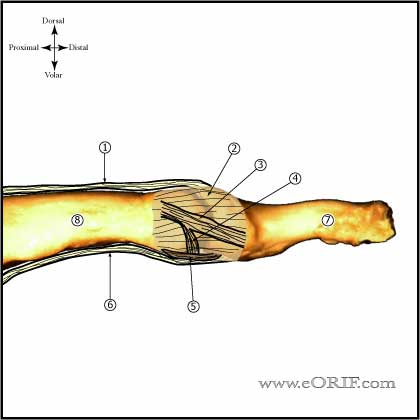
DIP Dislocation Anatomy
- Volar plate: often rupture from its proximal origin during dorsal dislocations, may prevent reduction.
- Dorsal dislocation is most common. Volar dislocation extremely rare.
- Impediments to reduction = volar plate, collateral ligaments, FDP tendon, thumb sesamoinds.
DIP Dislocation Clinical Evaluation
- Often occurs during ball catching sports.
- Evaluate for any open injury. DIP dilocations commonly have a transverse laceration in the flexion crease.
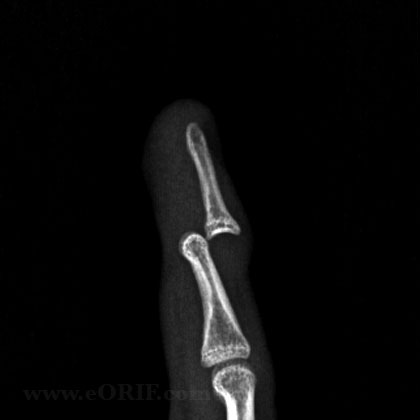
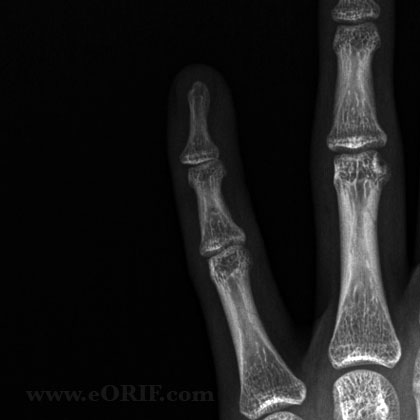
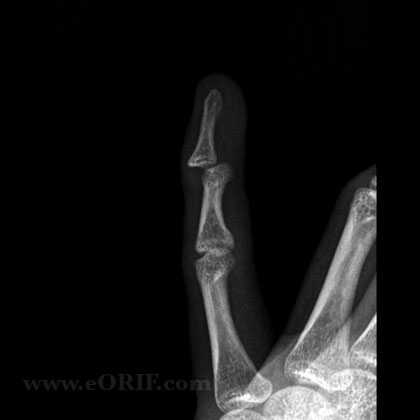
DIP Dislocation Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- A/P and lateral view of affected finger. Evaluate for any associated fracture
DIP Dislocation Classification / Treatment
- All closed DIP joint dislocations should be reduced as soon as possible. Simple longitudinal traction is attempted first for reduction. If unsuccessful attempt various PIP and DIP joint positions and rotations to allow any impediments to reduction to slide out of the joint.
- Closed Stableafter reduction: splint for comfort, start immediate ROM
- Closed Unstableafter reduction: immobilize in 20 degrees of flexion for 3-4 weeks followed to AROMChronic (>3 weeks old). Consider longitudinal 0.045 K-wire fixation for severe injuries or when aggressive rehab is required for adjacent injuries. Joint is fixed in neutral in both the A/P and lateral planes.
- Open: irrigation and debridement before and after reduction.
- Chronic (>3 weeks old): often requires open reduction via a dorsal transvers incision in the distal flexion crease with excision of interveaning scar tissue. Longitudinal extension of the incision proximally along the mid-axial line may be needed.
DIP Dislocation Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
DIP Dislocation Complications
- Stiffness
- Arthritis
- Hypersensitivity
- Infection / wound breakdown
DIP Dislocation Follow-up Care
- Repeat xrays at one week for confirm reduction is maintained.
- Remove K-wire at 3-4 weeks and begin AROM exercises.
DIP Dislocation Review References
Henry MH in Fractures in Adults 6th ed. |