|




|
synonyms: lateral condyle fracture, pediatric lateral condyle fracture,
Lateral Condyle Fracture ICD-10
A- initial encounter for closed fracture
B- initial encounter for open fracture
D- subsequent encounter for fracture with routine healing
G- subsequent encounter for fracture with delayed healing
K- subsequent encounter for fracture with nonunion
P- subsequent encounter for fracture with malunion
S- sequela
Lateral Condyle Fracture ICD-9
- 812.42(closed), 812.52(open)
Lateral Condyle Fracture Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- 10%-20% of all pediatric elbow fractures (Mirsky EC, J Orhtop Trauma 1997;11:117-120)
- lateral approach 5-6cm incision ; interval between brachioradialis and triceps (Badelon O, JPO 8;31:1988)
- tardy ulnar nerve palsies occur usually occur 20 yrs after lateral condyle fracture
Lateral Condyle Fracture Anatomy
- fall on outstretched arm with varus moment leads to avulsion of lateral condyle by the common extensor origin
Lateral Condyle Fracture Clinical Evaluation
- Fall onto outstretched hand or direct blow.
- Pain and swelling in the lateral elbow.
- Document NV exam before and after any treatment.
Lateral Condyle Fracture Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- A/P. lateral and oblique xrays
- Consider arthrography to assess intra-particular extention of fracture and adequacy of reduction. (Marzo JM, JPO 1990;10:317-321)
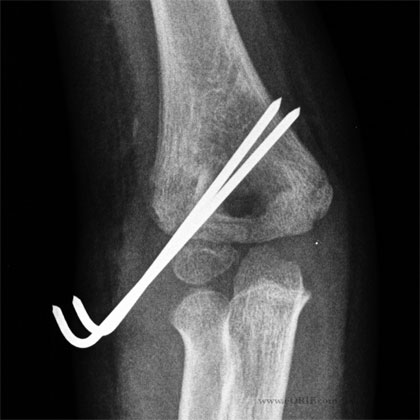
Lateral Condyle Fracture Classification / Treatment (Jakob R, JBJS Br 1975;57:430-436)
- Type 1 = nondisplaced; <2mm of fracture displacement. Generally stable if fracture does not extend into joint. RX=long arm posterior mold for 5days. XOP at 5 days. If Fracture remains unchanged LAC. F/U with XOP’s at 14 days. Continue with every 14-21 day XOP’s/LAC until fracture union. May require 8-12 weeks to achieve union. If >12wks, consider surgical fixation.
- Type 2=lateral displacement greater than 2mm, and the joint surface is usually disrupted. Rx=CRPP (Mintzer CM, JPO 1994;14:462-465) If conpression is needed across Fracture site consider pushing on fragment with the chuck end of a 4.5mm drill placed over the iniial K-wire. Also consider compression screw. Confirm reduction with arthrogram.
- Type 3 = significant displacement including radiocapitellar joint displacement. Rx=see Type 2.
- Open reduction via Kocher approach (tticeps-brachioradialis). Avoid dissection posterior to lateral condyle to preserve blood supply to capitellum.
Lateral Condyle Fracture Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
Lateral Condyle Fracture Complications
- nonunion, capitellar osteonecrosis, fishtail deformity of the distal humerus, premature growth arrest of capitellar physis, progressive lateral overgowth and cubitus varus, lateral prominence of the distal humerus
- excessive valgus of the elbow may lead to ulnar nerve palsy
- nonunion may lead to elbow instability, pain, and apprehension. Elbow ROM is typically well maintained.
Lateral Condyle Fracture Follow-up Care
- LAC for 4-6 weeks. K-wires are removed when there radiograhpic signs of union(3-6wks).
Lateral Condyle Fracture Review References
|






