|
synonyms:
Boutonniere Deformity ICD-10
Boutonniere Deformity ICD-9
- 842.13 (Sprains and strains of the interphalangeal joint)
- 736.21 (Boutonniere Deformity)
Boutonniere Deformity Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Caused by laxity, laceration or rupture of the central slip over the PIP joint in the finger. May occur with capsular distention from rheumatoid arthritis
Boutonniere Deformity Anatomy
- Central slip = the central portion of the extensor hood.
Boutonniere Deformity Clinical Evaluation
- PIP flexion, DIP extension deformity
- Elson test: used to diagnose central slip injury before deformity develops. Bend PIP joint 90 over edge of table and the extend middle phalanx against resistance. If central slip is injured PIP extension will be weak and DIP joint will be rigid. If central slip is normal DIP joint remains lax and PIP extension is strong.
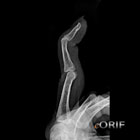
Boutonniere Deformity Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- Hand-finger views generally normal. Eval for proximal MP avulsion fracture.
Boutonniere Deformity Classification / Treatment
- Acute closed injury, no fracture: splint PIP joint in full extension for 6 week; followed by part-time splinted for additional 4 weeks. Must do active DIP extension/flexion ROM while it splint to avoid oblique retinacular ligament contracture
- Acute open laceration / bony avulsion: primary central slip repair
- Chronic injury, with full PROM: modified Fowler / Dolphin tenotomy vs Littler / Matev tendon graft reconstruction vs triangular ligament reconstruction
- Chronic injury, with contracture or arthritis: consider PIP arthrodesis
Boutonniere Deformity Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
Boutonniere Deformity Complications
Boutonniere Deformity Follow-up Care
Boutonniere Deformity Review References
|