|
synonyms:
Biceps Tenotomy Indications
- Biceps tendonitis in elderly low demand patients.
Biceps Tenotomy Contraindications
- Biceps tendonitis in a younger, physically active patient.
Biceps Tenotomy Alternatives
- Biceps Tenodesis
Typically used for elderly patients with low physical demands.
- Quicker recovery and earlier return to function than arthrodesis.
- Non-operative management
Biceps Tenotomy Pre-o p Planning / Special Considerations
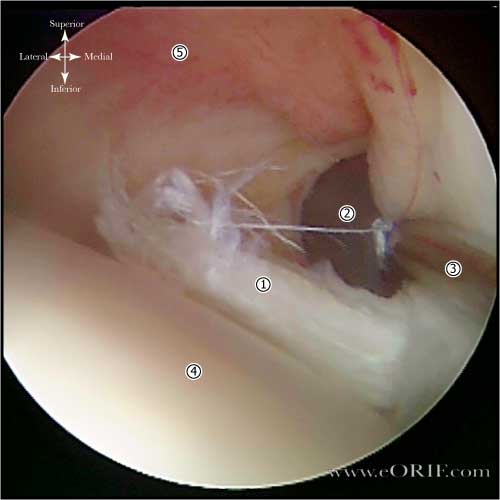
- Arthroscopic tenodesis with absorbable interference screw (Boileau Arthroscopy 2002:18:1002-1012)
- Percutaneous Intra-articular Trans-tendon technique: (Sekiya JK, Arthroscopy 2003;19:1137). Easily performed and does not require any supplemental hardware.
- Other techniques include: suture anchors, screw and soft tissue washer, keyhole technique.
- Arm postion for biceps tenodensis = 30 degrees flexion, 30 degrees IR, 30 degrees abduction. Elbow flexed to 90 degrees.
Biceps Tenotomy Technique
- Pre-operative antibiotics, +/- regional block
- General endotracheal anesthesia
- position. All bony prominences well padded.
- Examination under anesthesia.
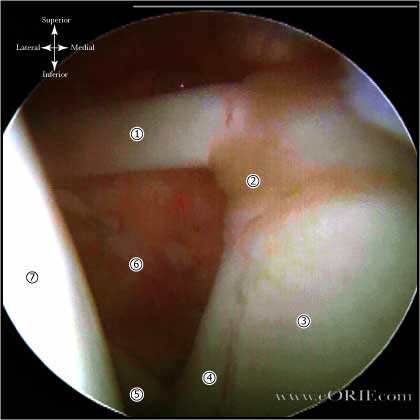
- Prep and drape in standard sterile fashion.Perform Shoulder Arthroscopy.
- Perform tenotomy of the tendon at is BLC insertion using an arthroscopic biter, or hooked cautery probe.
- Tendon is allowed to retract out of the glenohumeral joint.
- If biceps does not retract as a result of enlargement or attritional changes, the intraarticular portion of the biceps is resected allowing retraction out of the glenohumeral joint.
- Any associated pathology should be fixed concomittantly: RTC tear, Subacromial impingement, AC arthritis.
- Irrigate.
- Close.
Biceps Tenotomy Complications
- Patients may develop cosmetic deformity (Popeye muscle) post-operatively.
- Pain
Biceps Tenotomy Follow-up care
- Post-op: sling, immediate passive elbow and shoulder ROM, pendulum exercises, active wrist/hand ROM.
- 7-10 days: Continue sling. Started PT. Begin active shoulder motion without resistance. Avoid any resisted active elbow flexion / supination.
- 6 weeks: start muscle strengthening, active elbow flexion / supination.
- 3-6 months: Return to full activites
Biceps Tenotomy Outcomes
- 87% satisfied or very satisfied with the result in patients with full-thickness RTC tears(elderly or unrepairable tears). (Walch G JSES, 2005;14:238).
Biceps Tenotomy Review References
|

