 |
synonyms: ankle ATS, ankle scope, ankle arthroscopy
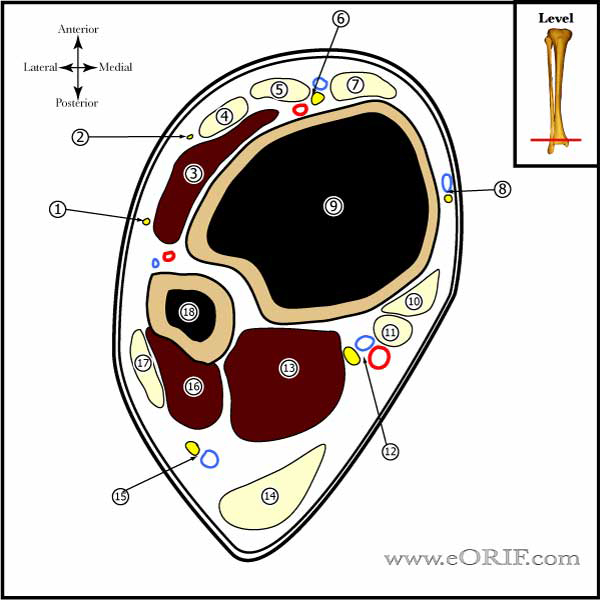
Ankle Scope Anatomy
Ankle Scope Pre-op Planning / Special Considerations
Articular Cartilage Grading
|
 |
synonyms: ankle ATS, ankle scope, ankle arthroscopy
Ankle Scope Anatomy
Ankle Scope Pre-op Planning / Special Considerations
Articular Cartilage Grading
|