synonyms:tibial shaft fracture external fixation, ex fix
Tibial Shaft Fracture External Fixation CPT
Tibial Shaft Fracture External Fixation Indications
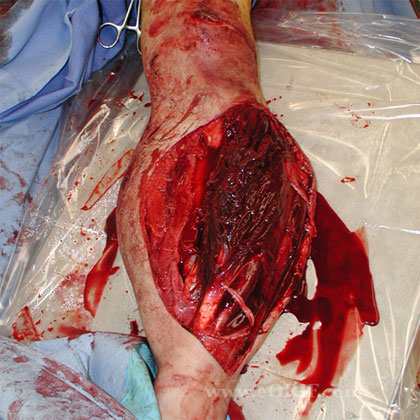
- High energy open fracture
- High energy pediatric fracture
- Open 3C tibial shaft fracture
- Unstable trauma patient
Tibial Shaft Fracture External Fixation Contraindications
Tibial Shaft Fracture External Fixation Alternatives
Tibial Shaft Fracture External Fixation Pre-op Planning
- Anterior unilateral frames are most effective, particularly when applied with relatively stiff components with a maximal spread between the pins in each main bony fragment. (Bebrens F,CORR 1983;178: 103).
- Predrilling and inserting pins manually prevents thermal necrosis and cracking.
- Avoid placement of pins within joint capsules. Knee capsule may extend 14mm distal to the tibial plateau.
- Conversion to intramedullary nail (when applicable) should be done within 2 weeks to decrease infection risk. (Bhandari M, JOT 2005;19:140).
- Converting external fixationto IM Nail: should be done within 7-10 days to minimize the risk of infection. Immediate conversion if without evidence of pin track infection. Delay of at least 4 days prior to conversion is recommended to allow resolution of the acute inflammatory phase and minimize risk of SIRS. (Della Rocca GJ, J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14(10 Spec No.):S131-5).
Tibial Shaft Fracture External Fixation Technique
- Sign operative site.
- Pre-operative antibiotics, +/- regional block.
- Supine position. All bony prominences well padded.
- General endotracheal anesthesia
- Prep and drape in standard sterile fashion.
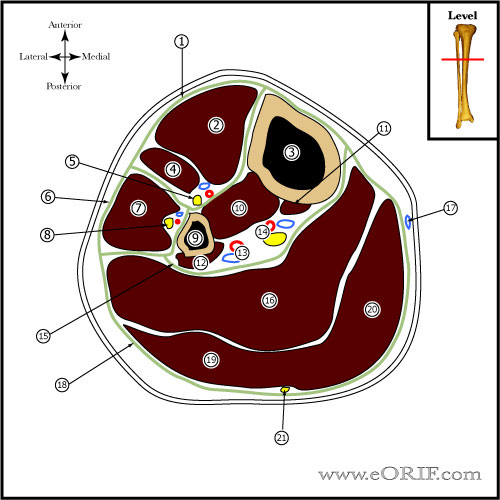
- 1-cm incision over preplaned pin site on anteriormedial border of tibia.
- Soft tissues incised to bone.
- Predrill using a tissue protector.
- Screw half pin in placed making sure that the pin penetrates both cortices.
- Ensure pin does not protrude more than 2mm of far cortex using fluoroscopy.
- Repeat for all half-pins.
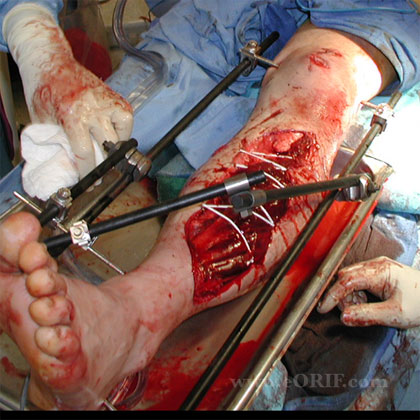
- Apply frame per manufacture recommendations / pre-op plan.
- Release any skin encroachmnet on the fixator pins.
- Dress pins with xeroform and 4x4's/
- Apply bulky Jones dressing with posterior mold to avoid equinus contracture.
Tibial Shaft Fracture External Fixation Complications
Tibial Shaft Fracture External Fixation Follow-up care
- Converting external fixationto IM Nail: should be done within 7-10 days to minimize the risk of infection. Immediate conversion if without evidence of pin track infection. Delay of at least 4 days prior to conversion is recommended to allow resolution of the acute inflammatory phase and minimize risk of SIRS. (Della Rocca GJ, J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14(10 Spec No.):S131-5).
- Post-op: NWB, Bulky Jones dressing with posterior mold to avoid equinus contracture. Pin site care.
- 7-10 Days: Evaluate for pin site infection, Review xrays for alignment, Continue Pin site care. Conversion to intramedullary nail should be done within 2 weeks to decrease infection risk. (Bhandari M, JOT 2005;19:140).
- 3 Weeks: Evaluate for pin site infection, Review xrays for alignment, Continue Pin site care.
- 6 Weeks: Evaluate for pin site infection, Review xrays for alignment, Continue Pin site care. Advance weight bearing when callus is seen on xray. Consider dynamizing frame. Plan frame removal.
- 2 Months: Remove frame if abundant callus seen on xray. Place in SLC.
- 3 Months: Review xrays, Cam walker / fracture brace
- 6 Months: Advance activity. Consider PT for any knee or ankle ROM limitations.
- 1Yr: follow-up xrays, assess outcomes.
Tibial Shaft Fracture External Fixation Outcomes
- (Rommens P, J Trauma 1989;29:630).
- 31 weeks to union, 18% malunion, for open tibia fractures treated with external fixation. (Aho AJ, CORR 1983;181:154).
Tibial Shaft Fracture External Fixation Review References