 |
synonyms: glenoid hypoplasia, glenoid dysplagia, dysplagia of the scapular neck
Glenoid Hypoplasia ICD-9
Glenoid Hypoplasia Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Failure of the inferior glenoid to ossify
- Incidence of glenoid hypoplasia ranges from 18% to 35%.
- Generally bilateral and symmetric
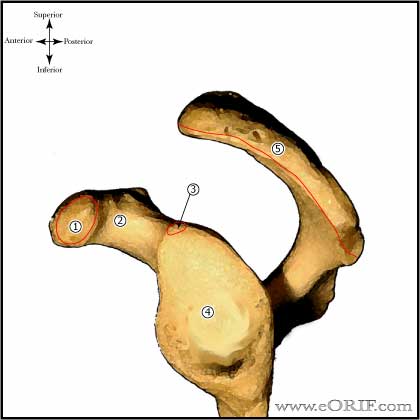
Glenoid Hypoplasia Anatomy
- Gleniod is formed by consolidation of the secondary centers of ossification of the superior glenoid, inferior glenoid and coracoid process.
Glenoid Hypoplasia Clinical Evaluation
- May have decreased abduction, decreased forward flexion, mild acillary webbing
- Multidirectional instability
Glenoid Hypoplasia Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- A/P and Lateral view in the plane of the scapula, and axillary view.
- West Point view: patient prone with arm in 90° abduction and neutral rotation. Xray beam is directed 25° posterior to the horizontal plane and 25° medial to the vertical plane. Useful for evaluating the anterior glenoid rim.
- CT scan is best to evaluate bony anatomy.
- MRI arthrogram (gadolinium): the anterior and posterior labrum are best seen on axial images and appear as dark triangular structures.
Glenoid Hypoplasia Classification / Treatment
- Treatment: PT with ROM and strengthening exercses focused on deltoid, RTC and parascapular muscles.
- Surgical treatment options: glenoid reaming, glenoid bone grafting, TSA, reverese TSA.
Glenoid Hypoplasia Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
- Skeletal dysplacia
- Mucopolysaccharidosis
- Holt-Oram Syndrome
- Apert's syndrome
- Cornelia de Lange's Syndrome
Glenoid Hypoplasia Complications
Glenoid Hypoplasia Follow-up Care
Glenoid Hypoplasia Review References
- °Smith S.P., Bunker T.D. Primary glenoid dysplasia. A review of 12 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(6):868–872.
- Wirth M.A., Lyons F.R., Rockwood C.A., Jr. Hypoplasia of the glenoid. A review of sixteen patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(8):1175–1184.
|

