 |
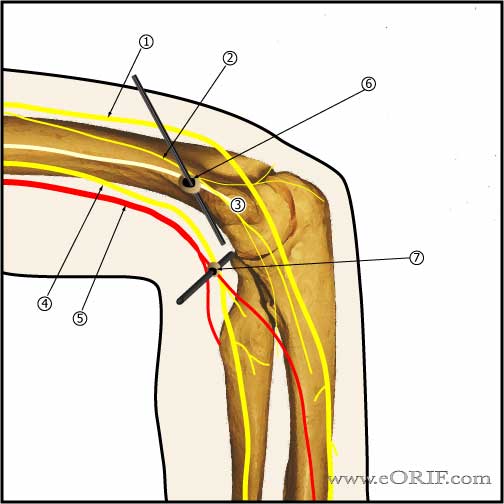
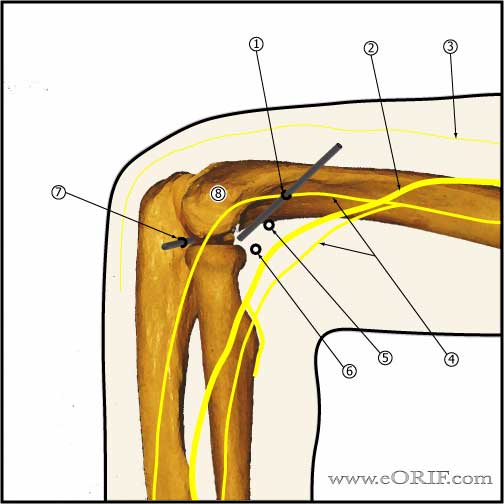
Standard Lateral Portals
- Proximal anterolateral portal: 2cm proximal and 1cm anterior to the lateral epicondyle. Lowest risk or radial nerve injury. (MIller C, JSES 1995;4:168).
- Radial Nerve
- Posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve
- Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve
- Midanterolateral portal
- Anterolateral portal: access to anterior joint (trochlea, coronoid process, coronoid fossa, medial radial head), placed exactly in the sulcus felt between radial head and capitellum anteriorly, elbow flexed 90°, capsule fully distended to displace NV structures anteriorly. Risks radial nerve.
- Mid-lateral portal: within soft spot in triangle formed by olecranon, lateral epicondyle, and radial head. Allows visualization of: inferior capitellum, inferior radioulnar joint. Risks:posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve.
- Lateral Epicondyle
|