|
v
|
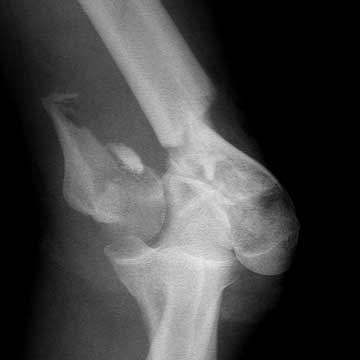
synonyms:distal humerus fracture ORIF, supracondylar humerus fracture ORIF
Distal Humerus Fracture ORIF CPT
Distal Humerus Fracture ORIF Indications
- Displaced intraarticular distal humerus fractures in adults
Distal Humerus ORIF Contraindications
- Medically unstable patients
- Active infection
- Excessive comminution (high velocity GSW)
Distal Humerus Fracture ORIF Alternatives
Distal Humerus Fracture ORIF Pre-op Planning / Special Considerations
- Document neurovascular status and the stateus of arm and forearm compartments pre-operatively.
- Consider olecranon osteotomy (Ring D, JOT 2004;18:446) vs paratricipital posterior approach (Schildhauer TA, JOT 2003;17:374).
- Posterior elbow approaches (Wilkinson JM, JSES 2001;10:380).
- Adequate exposure is critical. Surgical exposures: Triceps elevating, triceps splitting, triceps-reflecting anconeous pedicle approach, anconeus flap trasolecranon approach.
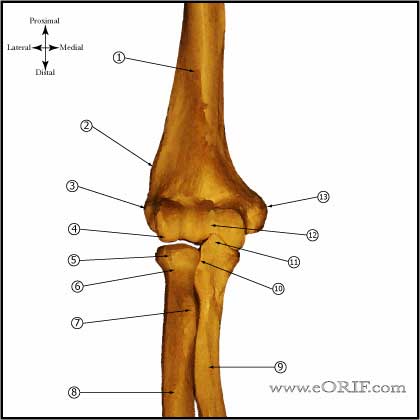
- Generally requires medial and lateral column plating. Parallel or 90-90 plates. (O'Driscoll SW, JSES 2005;14S:186S). (Sanchez-Sotelo J, JBJS 2007;89:961).
- posterior approach, olecronon osteotomy or triceps split. Olecranon osteotomy-chevron 2cm from tip of olecranon with saw exiting in bare area of the joint, the midportion of the trochlear fossa where the olecranon is devoid of cartilage.
- Majoriy of patients have ulnar nerve irritation post-op which improve by 1yr post opt. There is no difference in ulnar nerve symptoms, functional outcomes or complications for patients treated with either simple decompression or anterior transposition of the ulnar nerve at time of ORIF. (Schemitsch EH, ASES 2017 Specialty Day)
Distal Humerus Fracture ORIF Technique
- Pre-operative antibiotics, +/- regional block
- General endotracheal anesthesia
- Prone or lateral decubitus position. All bony prominences well padded.
- Arm supported on well padded post.
- C-arm images taken to ensure adequate films can be obtained.
- Prep and drape in standard sterile fashion.
- Padded sterile tourniquet place high on arm. Arm exasguinated and tourniquet inflated.
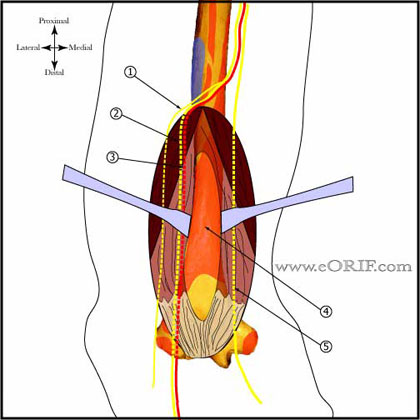
- Posterior longitudial incision curved around bony prominence of the olecranon.
- Ulnar nerve exposed and disected proximally to the medial intermuscular septum and distally to the flexor carpi ulnaris. Protect with Penrose drain.
- Triceps splinting approach: perform by splitting the triceps tendon in its midline from proximal to the proximal fracture line to the olecranon. If proximal extention is into the diaphysis the radial nerve must be exposed and protected.
- Olecranon osteotom approach: drill and tape proximal ulna for screw fixation. Generally 6.5mm or 7.3mm cannulated screw and washer. Perform apex distal chevron olecranon osteotomy at the bare spot (center of the olecranon sulcus indentified by elevating the anconeus). Perform final portion with osteotome.
- Fracture fragments exposed and cleared of clot preserving any soft tissue attachments.
- Articular fragments reduced anatomically and temporarily held with K-wires / large pointed tenaculum clamp.
- Longitudinal traction applied with a Mersilene tape passed over the trochlear notch of the ulna.
- Two 4.0 cannulated screws placed from medial to lateral, countersunk in the ulnar sulcus.
- Reconstructed articular surface is then reduced to the distal humeral metaphysis.
- Plate lateral column posteriorly and medial column medially using pre-countured periarticuar plates (Synthes, Acumed, Zimmer).
- Irrigate.
- Place drain.
- Repair triceps split with 0 Vicryl sutures.
- Close in layers.
Distal Humerus Fracture ORIF Complications
Distal Humerus Fracture ORIF Follow-up care
- Post-op: Posterior splint, NWB.
- 7-10 Days: Remove splint, begin passive shoulder and elbow ROM. Stress elbow ROM. Active flexion, gravity extension. Active extension avoided for 6wks. Generally start physical therapy for ROM and strengthening
- 6 Weeks: Begin active extension, strengthening exercises provided fracture union is evident on xray.
- 3 Months: Ensure full restoration of shoulder and elbow ROM. Consider bone stimulator if union is delayed. Sport specific rehab.
- 6 Months: return to full activities / sport.
- 1Yr: Follow-up xrays, assess outcomes.
- Outcome after ORIF of intra-articular fx’s= Mean flexion contracture-25 degress, mean arc of motion-108 degrees, @75% of normal strength. 24% reoperation usually for HWR (McKee JBJS 2000;82A:1701).
- Elbow Outcome Measures.
Distal Humerus ORIF Outcomes
- 84% Good/excellent, ROM = 26° to 125°. (Sanchez-Sotelo J, JBJS 2007;89A:961).
- 87% Good/excellent, ROM = 23° to 129° (Doornberg JN, 2007;87A:1524).
- Mean flexion contracture-25 degress, mean arc of motion-108 degrees, @75% of normal strength. 24% reoperation usually for HWR (McKee JBJS 2000;82A:1701).
- 100% union, 48%required second operation(contracture/ulnar neuropathy/hardware removal/loss of fixation). Average arc of ulnohumeral motion was 96° (range, 55° to 140°). Mayo Elbow Performance Score results = 19% excellent, 57%good, 24%fair. (Ring D, JBJS 2003;85A:232).
- ROM 24° to 131° , Mean Mayo Elbow Performance Score =93 (100=maximum). (Kamineni S, JBJS 2004;86A:940).
- (Sanchez-Sotelo J, JBJS 2007;89:961)
Distal Humerus ORIF Review References
|




